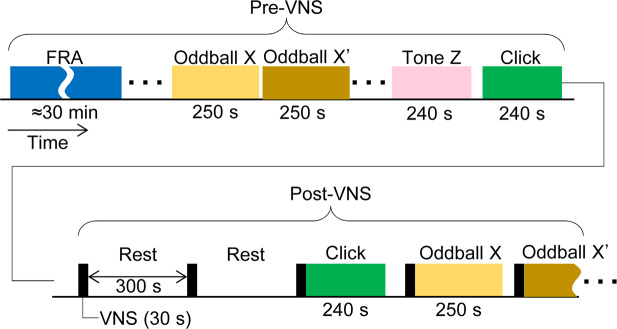
Figure 1.
Experimental procedure. The experiments consisted of two main conditions: pre- and post-VNS. The pre-VNS sessions completed prior to VNS and always preceded the post-VNS sessions to avoid confounding the effect of VNS. During post-VNS sessions, 30-s period of VNS was made with an interval of 300 s (5 min). AEPs were characterized in the click sequence, tone sequence, oddball paradigm, etc., each test block of which was designed to be shorter than 5 min. Each oddball paradigm consisted of 2 blocks; in the second block (oddball X′), the tones frequencies of standard and deviant stimuli were inverted from those in the first block (oddball X). Tone sequences of an arbitrary tone burst (Tone Z), whose frequency was close to CF at the test shank, were used to characterize CSD. Prior to the main experiments, we characterized FRA and identified the CF at each of the recording sites in the auditory cortex and thalamus. VNS, vagus nerve stimulation; AEP, auditory evoked potential; FRA, frequency response area; CF, characteristic frequency; CSD, current source density.