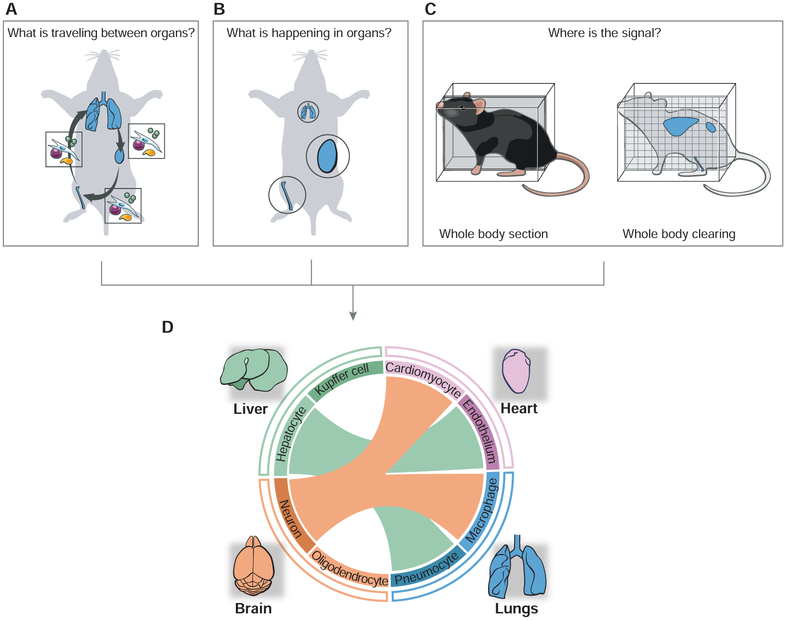
Figure 2. Studying immunological processes at the scale of the whole body.
(A-C) Schematics illustrating the fundamental challenges associated with studying inter-organ signaling. The three upper panels illustrate how to identify the mediators of inter-organ communications and their impacts on organ states. In A, the boxes illustrate the molecular and cellular mediators of inter-organ communications – using lungs, bone and kidney as a hypothetical network of communicating organs. In B, organs involved in a systemic communication circuit are shown in circles whose size is proportional to a given activity or effector mechanism. In C, organism-wide imaging is illustrated using as examples whole-body sectioning or clearing.
(D) Towards organism-level analyses of immune circuitry and its integration with host physiology. Data obtained through the approaches listed above (A-C) are integrated as a hypothetical inter-organ network, which is represented as a circular plot with links (colored lines) between communicating organs (outer circle) and cell types (inner circle) within each organ. The color of the lines linking organs depicts the sender organ.