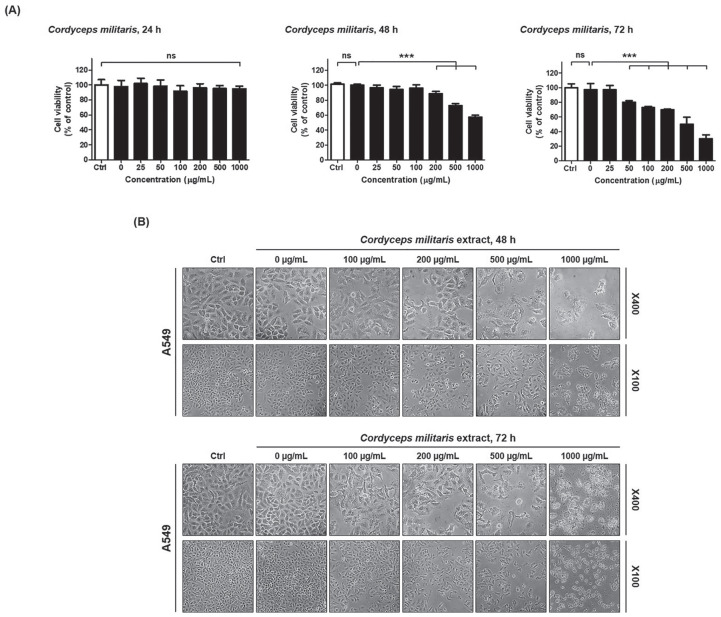
Figure 1.
(A) Cell viability after treatment with Cordyceps militaris for 24 hours, 48 hours, and 72 hours. (B) Detection of morphological changes by C militaris treatment for 48 hours and 72 hours. Cordyceps militaris dose- and time-dependently inhibits cell proliferation and induces morphological changes in A549 cells (non–small lung cancer cells). (A) Inhibition of the growth of A549 cells by C militaris. A549 were exposed to 0 (vesicle), 25, 50, 100, 200, 500, and 1000 µg/mL C militaris extract for 24 hours, 48 hours, and 72 hours prior to estimation of cell number using the CCK-8 assay. The experiment was performed in triplicate. C militaris significantly inhibited cell proliferation of A549 cells. (B) Morphological changes of A549 cells treated with C militaris compared with control (vehicle). Microscopic images of A549 treated with C militaris for 48 hours and 72 hours. Magnification ×100 and ×400. The statistics demonstrated that the percentage of the cells mainly represents treated cells, which was apparent when the percentage of control cells markedly decreased. Data are presented as means ± standard deviations from triplicate experiments. Statistical significance was considered as ***P < .001 versus vehicle treatment; ns, nonsignificance.