Figure 1.
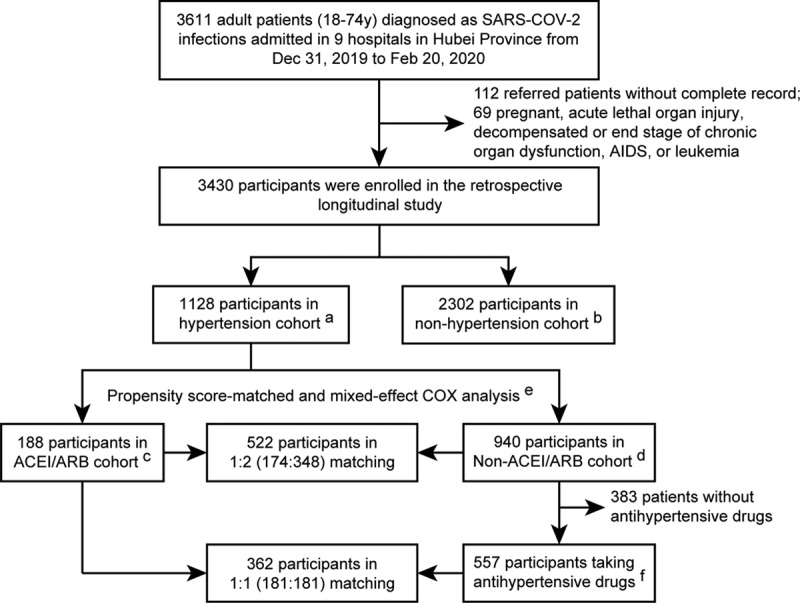
The flowchart showing the strategy of participant enrollment. a, 1128 participants with a history of hypertension enrolled in the hypertension cohort. b, 2302 participants without a history of hypertension enrolled in the nonhypertension cohort. c, 188 patients with hypertension who taking ACEI (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor) or ARB (angiotensin II receptor blocker) during hospitalization were enrolled in the ACEI/ARB cohort. Patients discontinued treatment of hypertension due to inability to take medications or hypotension were not excluded from the cohort. d, 940 patients with hypertension who never taking ACEI and ARB during hospitalization were enrolled in the non-ACEI/ARB cohort. e, Propensity score-matched age, gender, cough, dyspnea, comorbidities (diabetes mellitus, coronary heart disease, and chronic renal disease), chest computerized tomography (CT)-diagnosed lung lesions, and incidence of increased CRP (C-reactive protein) and creatine. Hospital site as a random effect in the mixed-effect Cox model. f, 557 patients with antihypertension drug who never taking ACEI and ARB during hospitalization were enrolled in the secondary non-ACEI/ARB cohort. SARS-COV-2 indicates severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
