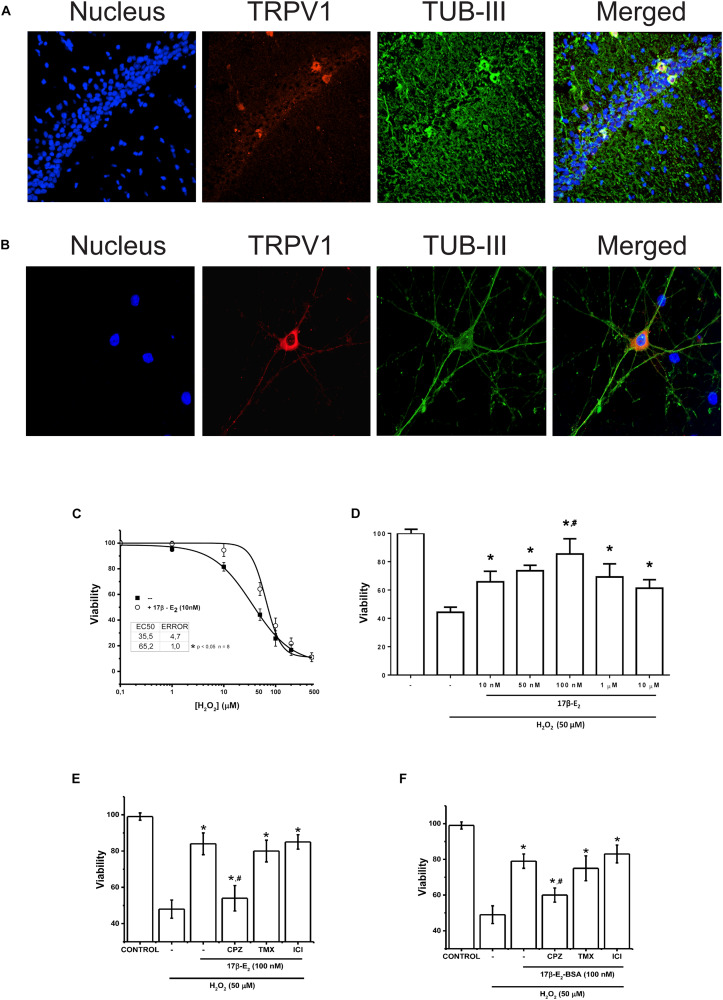
FIGURE 4.
Membrane activity of TRPV1 is sufficient condition to run 17β-estradiol protection against oxidative stress. (A) Immunostaining for TRPV1 expression in rat hippocampus. The technique selectively detected the CA3 region of hippocampus. (B) TRPV1 detection in 7-day cultured hippocampal neurons. (C) Changes in cell viability after 24 h incubation with H2O2 at increasing concentrations in presence and absence of 17β-estradiol in primary culture of hippocampal neurons. (D) Bar graph summarizes the effect of increasing doses of 17β-estradiol over H2O2 50 nM (N = 3) (E) Bar graph shows the effect of 10–7 M of 17β-estradiol on 5 × 10–5 M of H2O2 in hippocampus-derived neurons (N = 5). (F) The graph summarizes the effect of the impermeable adduct 17β-estradiol-BSA, 10–7 (17β-estradiol-BSA) on cell death induced by 5 × 10–5 M of H2O2 (N = 3). CPZ: capsazepine (10 μM); TMX, inhibitor of estrogen receptor α tamoxifen (10–6 M); ICI, inhibitor of estrogen receptor β ICI 182780 (10–6 M). Results are expressed as data normalized to untreated condition (UT) (without H2O2 or 17β-estradiol). Bars indicate means ± SD. Statistical differences correspond to one-way analysis of variance and Bonferroni’s post hoc test. #P < 0.05 vs. 17β-estradiol CPZ; *P < 0.01 vs. 17β-estradiol H2O2.