Fig. 11.6.
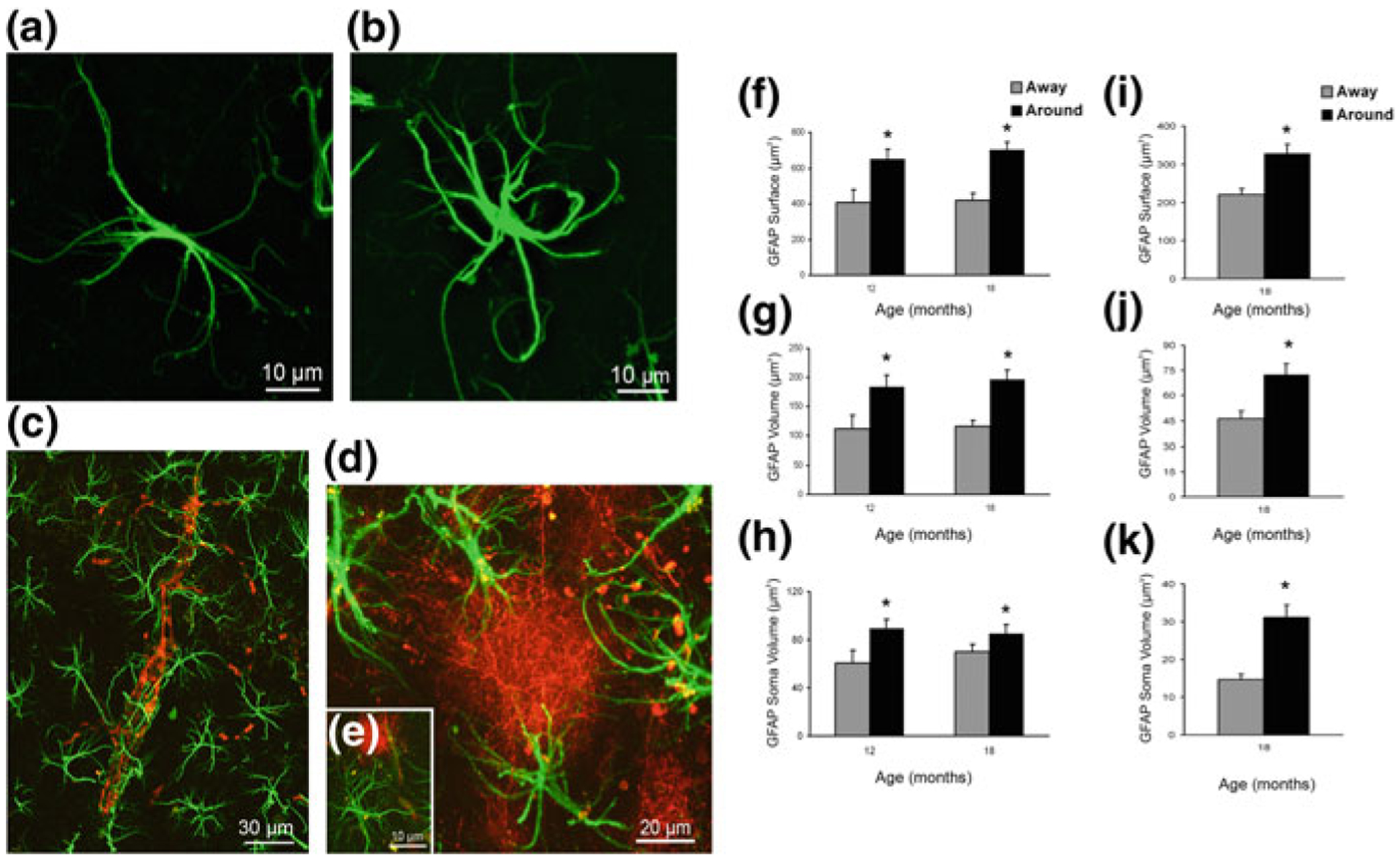
Concomitant astroglial atrophy and astrogliosis at the advanced stages of AD-like pathology in 3xTg-Ad mice. a, b Confocal images of hippocampal preparations dually labelled by GFAP and by anti-β amyloid monoclonal antibody illustrating differential changes in GFAP profiles in astrocytes distant to the plaques (a) and associated with the β-amyloid plaques (b). c–e Confocal dual labelling images (GFAP in green and β-amyloid in red) in 3xTg-AD mice showing the accumulation of astrocytes around the β-amyloid plaques and vascular β-amyloid deposits. Astrocytes surrounding β-amyloid plaques (d, e) and β-amyloid deposits around a blood vessel (c), undergo astrogliosis. f–k Bar graphs showing GFAP-positive astrocytic surface area (f), volume (g) and somata volume (h) differences between astrocytes located around the β-amyloid plaques (Aβ) and those distant to the plaques in the CA1 of 3xTg-AD animals. i–k Similar astrocytic surface area (i), volume (j) and somata volume (k) differences are observed in the DG at 18 months of age. Bars represent mean 6 SEM (p < 0.05). Reproduced with permission from [203]
