Figure 6.
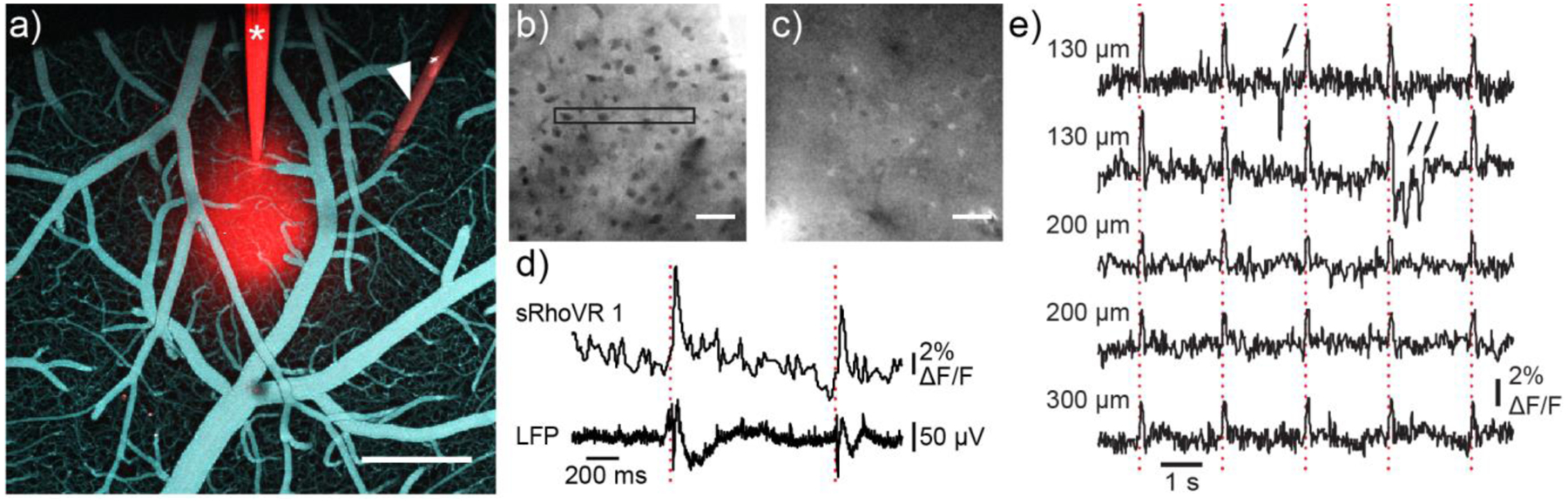
Two-photon voltage imaging in mouse cortex with sRhoVR. sRhoVR (100 to 200 μM in ACSF) was pressure-injected through a glass or quartz micropipette into layer 2/3 of the barrel cortex of an anesthetized mouse. a) A view from the top on the cortical surface after intracortical injection of sRhoVR (red) and intravascular injection of fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated dextran (cyan); the sRhoVRfilled glass pipet (asterisk) and tungsten electrode (white arrowhead) are visible. Scale bar, 500 μm. b) Typical two-photon images of tissue staining with sRhoVR in cortical layer 2/3 in b) anesthetized or c) awake mice. Black rectangle depicts a typical region of interest (ROI) for data acquisition. d) Time-course of sRhoVR fluorescence, relative to baseline (ΔF/F), and local field potentials (LFP) traces acquired simultaneously in anesthetized mouse. Dotted red lines indicate timing of contralateral whisker pad stimulation with a single 300 μs weak electrical pulse. e) Time-courses of sRhoVR fluorescence relative to baseline (ΔF/F) in awake mouse; each traces corresponds to a different ROIs in the same animal at the indicated cortical depth. Dotted red lines indicate timing of contralateral whisker pad stimulation with a single air puff. Black arrows point to motion artifacts.
