Figure 3.
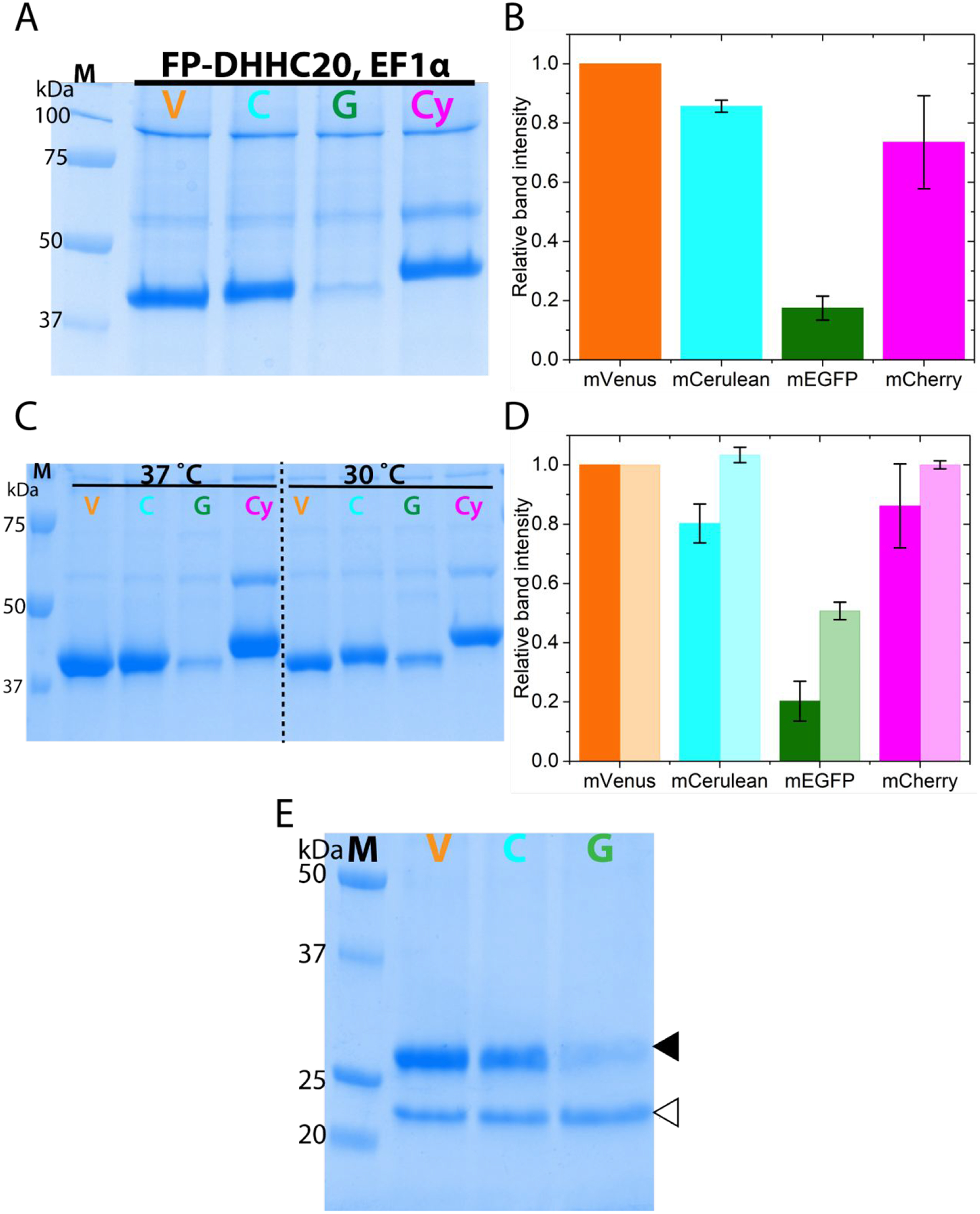
N-terminally fluorescent protein tagged DHHC20 expression under different promoter and using baculovirus mediated over-expression (A) SDS-PAGE analysis of FP-DHHC20 over-expression driven by the elongation factor 1 alpha (EF1α) promoter in HEK293T cells (B) Quantitation of the relative protein levels of FP-DHHC20 expressed using EF1α promoter. (C) SDS-PAGE analysis of metal affinity purified N-terminal FP tagged DHHC20 expressed using baculovirus in HEK 293S GnTi− cells at 37 and 30°C. (D) Quantitation of relative expression levels for N-terminal tagged DHHC20 at 37 (dark fill) and 30°C (light fill). (E) SDS-PAGE analysis of N-terminal FP tagged DHHC20 expressed at 37°C purified using an anti-GFP nanobody resin. The DHHC20 protein (filled triangle) is eluted from the nanobody resin by cleaving it off from the fluorescent protein by the PreScission protease (empty triangle). mVenus-DHHC20, V; mCerulean-DHHC20, C; mEGFP-DHHC20, G; mCherry-DHHC20, Cy. Values in bar graphs are mean±sd of two independent experiments.
