Fig. 5. mtDNA and cGAMP prevent endothelial proliferation through inhibition of YAP.
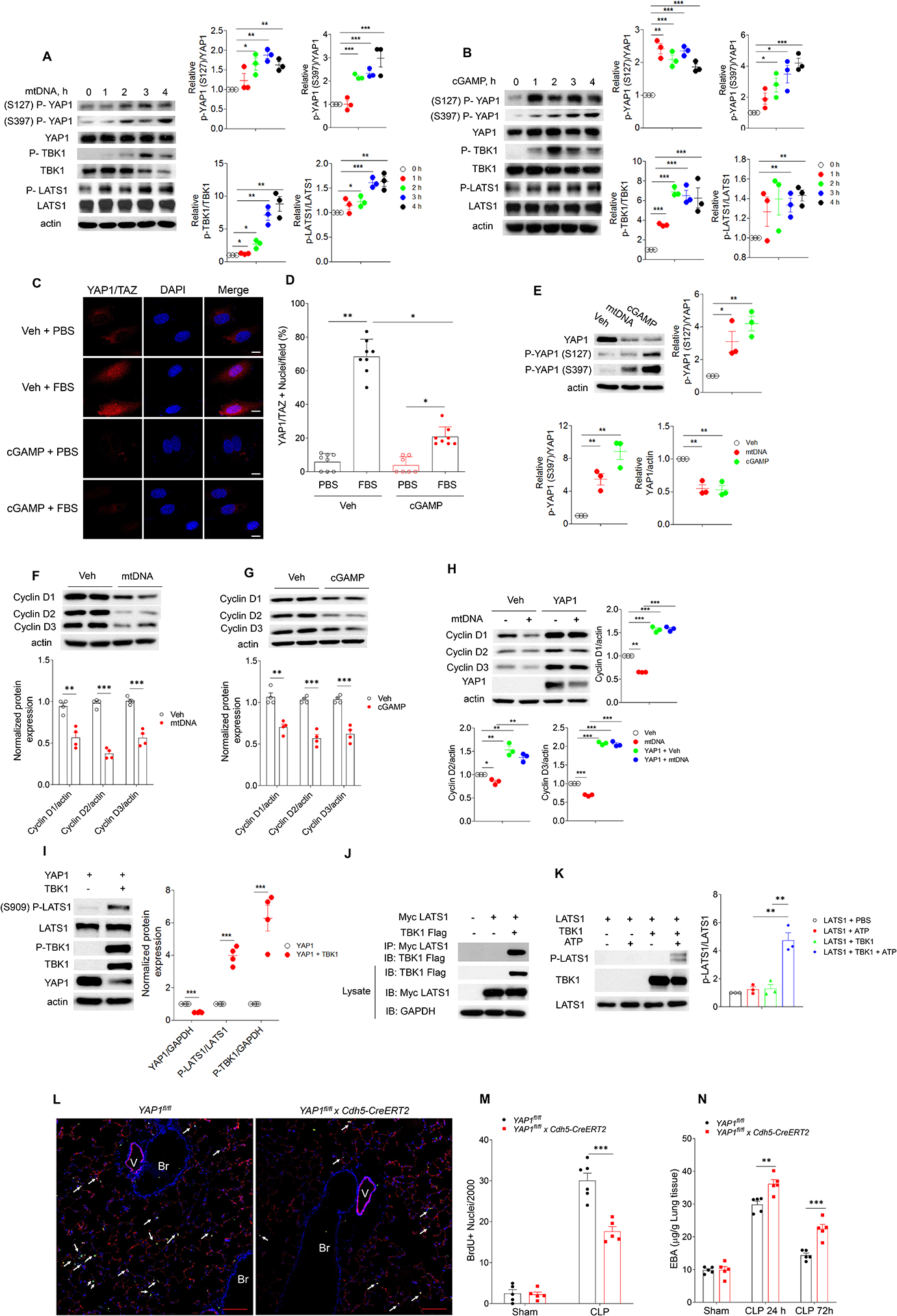
(A, B) Immuno blot of protein expression in hLMVECs with transfection of mtDNA (3 μg/ml, 0–4h, A) or cGAMP (3 μg/ml, 0–4h, B), n = 3. (C, D) hLMVECs with cGAMP (3 μg/ml, 20h) transfection were challenged with 10% FBS for 1 h, and the YAP1-TAZ nuclear translocation in hLMVECs were analyzed by Immunofluorescence staining. (C) Representative image and (D) percentage of hLMVECs with YAP1-TAZ nuclear trans-localization with FBS challenge. Values are shown as mean ± SD; data were obtained from three independent experiments, n= 7–8. (E) Immuno blot analysis YAP1 phosphorylation and YAP1 expression in hLMVECs with transfection of mtDNA (3 μg/ml, 20h) or cGAMP (3 μg/ml, 20h), n=3. (F, G) Expression of cyclin D1,D2, D3 in hLMVECs transfected with mtDNA (F) or cGAMP (G) (3 μg/ml, 20h), n = 3. (H) YAP1 restores mtDNA induced decrease of cyclin D1, 2, 3 expression in hLMVECs. Control plasmid or YAP1 plasmid (3 μg/ml, 48h) transfected hLMVECs were transfected with mtDNA (3 μg/ml) for 20h, the expression of cyclin D1, 2, 3 were analyzed by immunoblotting, n = 3. (I) Transfection of TBK1 induces LATS1 phosphorylation. HEK293T cells were co-transfected with plasmids encoding TBK1 and YAP1 (3 μg/ml, 48h) before immunoblotting analysis, n = 4. (J) HEK293 cells were co-transfected with myc-tagged LATS1 (myc-LATS1) and either vector control (Vector), Flag-tagged TBK1 (Flag-TBK1). LATS1 was immunoprecipitated to assess the binding proteins by immunoblotting. Input lysates were used to blot protein and verify the transfected protein expression. Representative images from three independent experiments, n = 3. (K) IP-purified myc-LATS1 (Myc-LATS1) from myc-LATS1 transfected HEK293 cells was co-incubated with IP-purified Flag-TBK1 from Fag-TBK1 transfected HEK293 cells. Purified proteins were used for in vitro kinase assay. Phosphorylated LATS1 (S909) was analyzed via immunoblotting and quantitated via densitometry, n = 3. (L-N) Endothelial cell specific deletion of Yap1 (Yap1fl/fl x Cdh5-CreERT2) in mice prevents endothelial regeneration and recovery from lung injury. Yap1fl/fl mice were crossed with Cdh5-CreERT2 to delete YAP1 in endothelial cells. After tamoxifen induced deletion of Yap1, mice were used for CLP. (L) Representative micrographs from three independent experiments showing endothelial cell (EC) proliferation in lungs from Yap1fl/fl and Yap1fl/fl x Cdh5-CreERT2 mice at 72h post CLP. Green, anti-BrdU; Red, anti–CD31; Blue, DAPI. Arrows indicate proliferating endothelial cells. Scale bar, 200 m. Br indicates bronchia; V, vessel. (M) Graphic presentation of increased proliferating endothelial cells in Yap1fl/fl as compared to Yap1fl/fl x Cdh5-CreERT2 lungs post-CLP, n = 5. (N) Lung transvascular permeability measurement following CLP showed defective recovery in Yap1fl/fl x Cdh5-CreERT2 as compared to Yap1fl/fl mice, n = 5. Data are shown as mean ± SD. * P < 0.05, * * P < 0.01, * * * P < 0.001, two-tailed t-test. Please also see Figure S2, 4 & 5.
