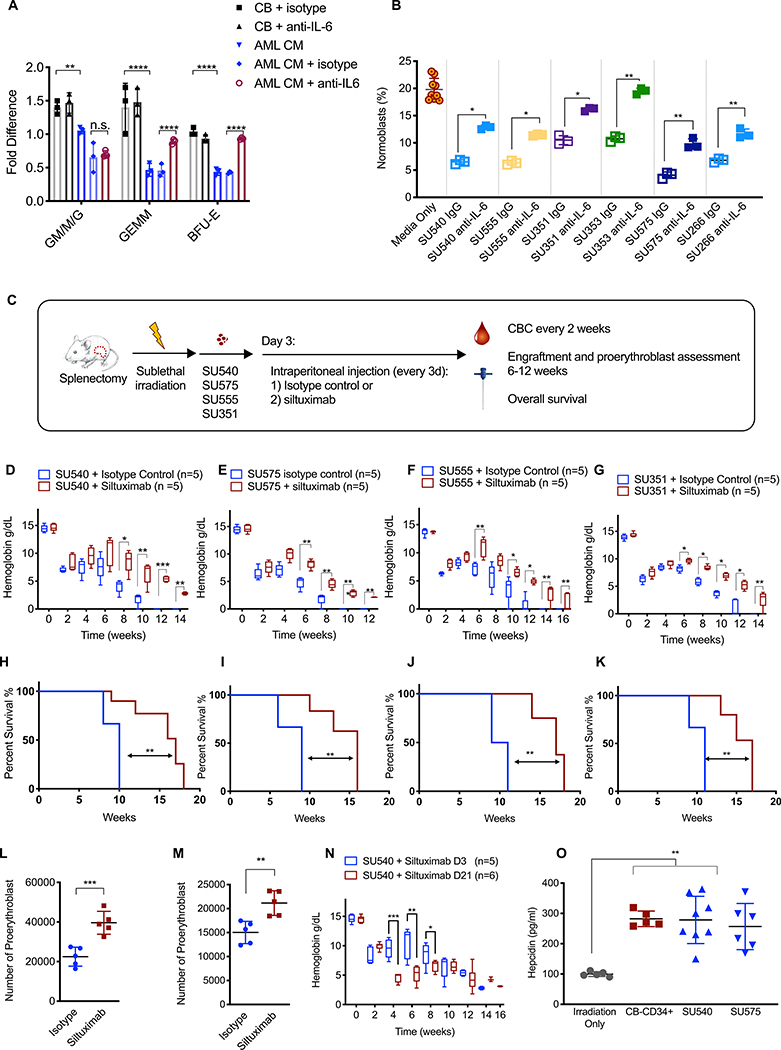
Fig. 7. Human AML suppresses erythroid differentiation and causes anemia via paracrine effects of IL-6.
(A). Fold change in the number of colonies generated by normal human CB-CD34+ cells in the presence of CB-CD34+-CM (n=3) or human AML-CM (n=3) +/− human IL-6 neutralizing antibody or an isotype control antibody. The number of colonies was normalized to either CB-isotype control or AML-CM isotype controls as indicated by brackets in the figure. (B). Transwell assay for erythroid differentiation was done in the presence or absence of a human IL-6 neutralizing antibody or an isotype control antibody. Aliquot of cells from the top compartment was analyzed for the percentage of CD71+GPA+ normoblasts on day 6. (C). Schematic of experimental procedure. Treatment with control antibody or siltuximab (anti-human IL-6, 20 mg/kg) began on day 3 and occurred every 3 days. Hemoglobin in NSGspln- mice engrafted with primary AML (D) SU540, (E) SU575, (F) SU555, and (G) SU351. Overall survival in NSGspln--PDX mice engrafted with (H) SU540 10 weeks vs 17 weeks p=0.02, (I) SU575 9 weeks vs 16 weeks, p=0.002, (J) SU555 10 weeks vs 17 weeks p=0.0014, and (K) SU351 11 weeks vs 16 weeks, p=0.006). Absolute numbers of CD71+/GPA+ normoblasts in NSGspln--PDX mice engrafted with (L) SU555 2.25×104 vs 3.96×104 p=0.0009 and (M) SU351 1.50×104 vs 2.11×104 p=0.004. (N) Hemoglobin in NSGspln--SU540 mice which began treatment on d3 versus d21. (O) Serum hepcidin concentrations in control, NSGspln--PDX engrafted with SU540 or SU575, and NSGspln--CB-CD34+ mice (n=5 for each group, p=0.001). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001