Figure 1.
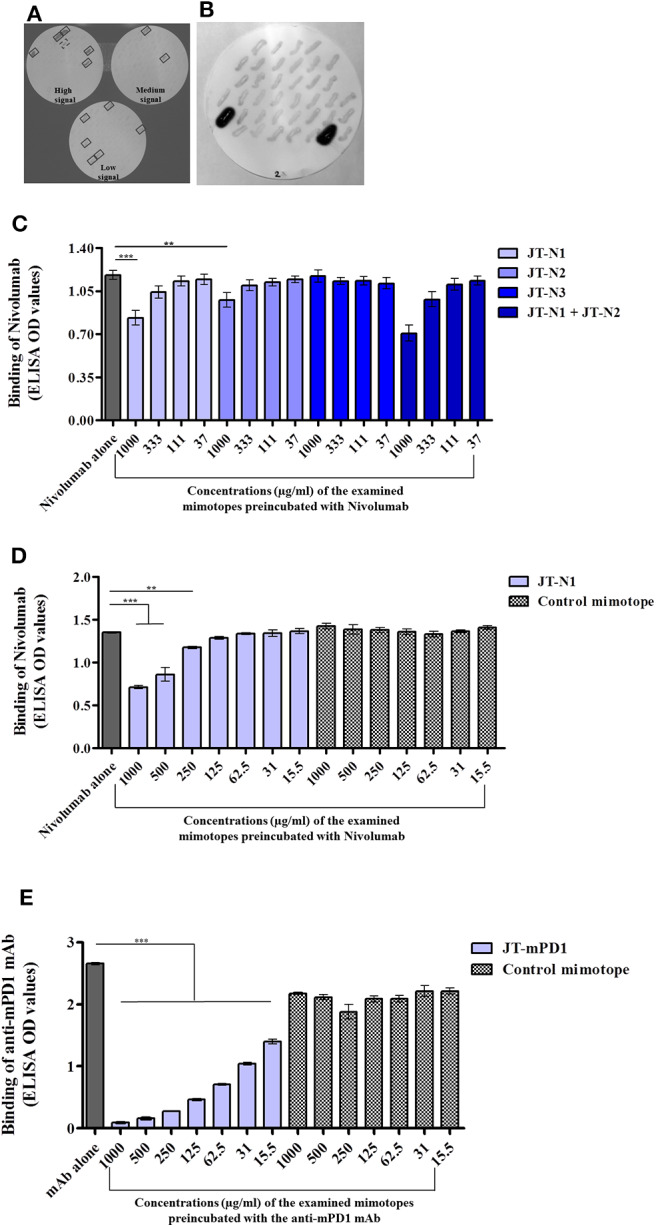
Identification of the mimotopes of the anti-human programmed cell death 1 (hPD1) mAb Nivolumab and anti-mouse PD1 (mPD1) monoclonal antibody (mAb), and examination of their specificity. Colony blot assay was applied on clones of Escherichia coli individually expressing overlapping peptides spanning the entire extracellular domain of hPD1 (A) or mPD1 (B) with anti-hPD1 and anti-mPD1 mAbs used for detection, respectively, as described in the Materials and Methods section. In the colony blot assay with anti-hPD1 mAb, the detected clones are boxed with solid line. One positive clone with failed sequencing is boxed with a broken line. Capacity of the identified mimotopes JT–N1, JT–N2, and JT–N3 (C,D) and JT–mPD1 (E) with comparison to a control mimotope, in inhibiting the binding of anti-hPD1 and anti-mPD1 mAbs to recombinant hPD1 or mPD1 proteins, respectively, is shown. Recombinant hPD1 or mPD1 proteins were used for coating in a solid phase-based assay (ELISA), and binding of the respective mAbs to the coated proteins was evaluated alone or after preincubation with different examined concentrations of the respective mimotopes. The results are representative of at least two repeated experiments. Significant differences are indicated by asterisks (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).
