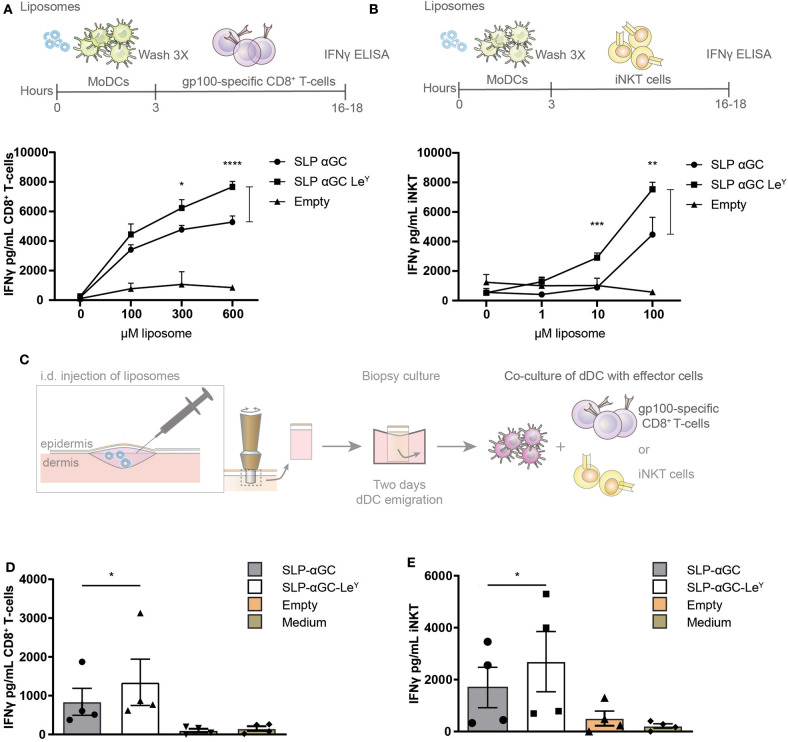
Figure 4.
Incorporation of LeY in liposomes increases CD8+ T-cell and iNKT activation by liposome-exposed moDC and human skin DC. (A) Data showing activation of gp100 specific T-cells as measure of IFNγ secretion after co-culture with moDC loaded with different concentrations of non-targeting and targeting LeY liposomes. Concentrations used as indicated in the figure. Data shown as mean ± SD of technical triplicate and representative of n = 5, one-way ANOVA, Tukey's post hoc test, * < 0.05 **** < 0.0001. (B) Secretion of IFNγ by human iNKT cells after co-culture of moDC with unmodified and LeY liposomes. Concentrations used as indicated in the figure. Data shown as mean ± SD of technical triplicate and representative of n = 5, one-way ANOVA, Tukey's post hoc test, ** < 0.01 *** < 0.001. (C) Schematic overview of experiment set-up for gp100 specific T-cell and iNKT activation by emigrated DC after liposome injection in human skin explants. Migrated skin DC were co-cultured with gp100 specific CD8+ T-cell and iNKT for 16–18 h after which IFNγ was measured in supernatant (D) IFNγ secretion of gp100 specific CD8+ T-cells after co-culture with a mixture of migrated skin-emigrated DC. Data represents mean ± SEM n = 4, ratio paired t-test, * < 0.05). (E) IFNγ release by iNKT after co-culture with a mixture of migrated skin-emigrated DC. Data is shown as mean ± SEM n = 4, ratio paired t-test, * < 0.05.