FIGURE 1.
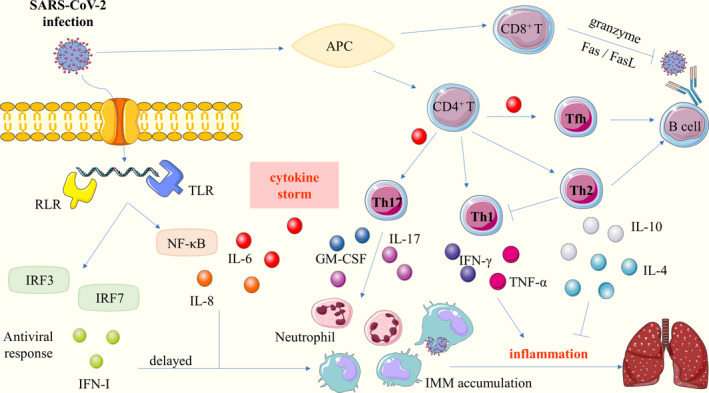
SARS‐CoV‐2 infection‐induced immune responses. SARS‐CoV‐2 enters the host cells though binding to cellular receptors ACE2. After SARS‐CoV‐2 infects cells, the innate immune response begins with the recognition of pathogen‐associated molecular patterns by the RLR and TLR. It activates IRF3, IRF7 and NF‐κB that lead to antiviral response and the production of inflammatory cytokines, respectively (left panel). With the assistance of APC, activated T cells exert different immune effects by distinct immune effector molecule (right panel). The innate and T cell immune responses eventually lead to the recruitment of IMM and neutrophil in the lung, and release high amounts of cytokines that mediate inflammatory damage
