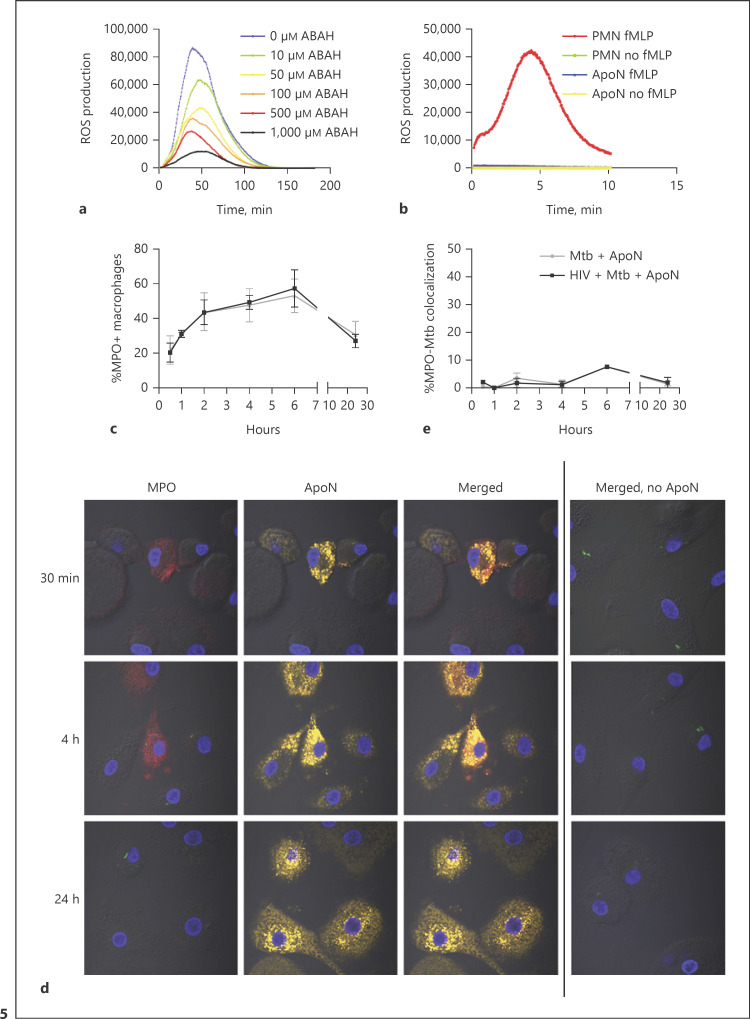
Fig. 5.
MPO, which is active even after apoptosis, is present in macrophages which have ingested apoptotic neutrophils (ApoN). ROS production by apoptotic neutrophils was measured through chemiluminescence upon stimulation with PMA (a) or fMLP (b), showing the mean from 3 independent experiments. a MPO was inhibited by 30 min of preincubation with increasing concentrations of ABAH (as indicated) before luminol and PMA was added to the apoptotic neutrophils. b Freshly isolated neutrophils (PMN) and apoptotic neutrophils were stimulated with fMLP and their ROS production measured in the presence of luminol. c Percentage of MPO+ macrophages at the indicated time points, as quantified by microscopy (d). e Percentage of MPO colocalization with M. tuberculosis (Mtb) phagosomes at the indicated time points. The macrophages were first infected with HIV followed by M. tuberculosis (MOI = 2) infection for 1.5 h, washed, and stimulated with apoptotic neutrophils for up to 24 h. The graph shows the mean ± SEM from 2 independent experiments. d The microscopy images visualize the macrophages by DIC, while apoptotic neutrophils are shown in yellow, M. tuberculosis-GFP in green, MPO in red, and DAPI in blue. The first row shows the cells 30 min after the addition of apoptotic neutrophils, the second after 4 h, and the last one after 24 h. The last column shows infected macrophages that have not been stimulated with ApoN but have been stained for MPO.