Figure 2. Rate of small molecule and hydrogel degradation in response to light.
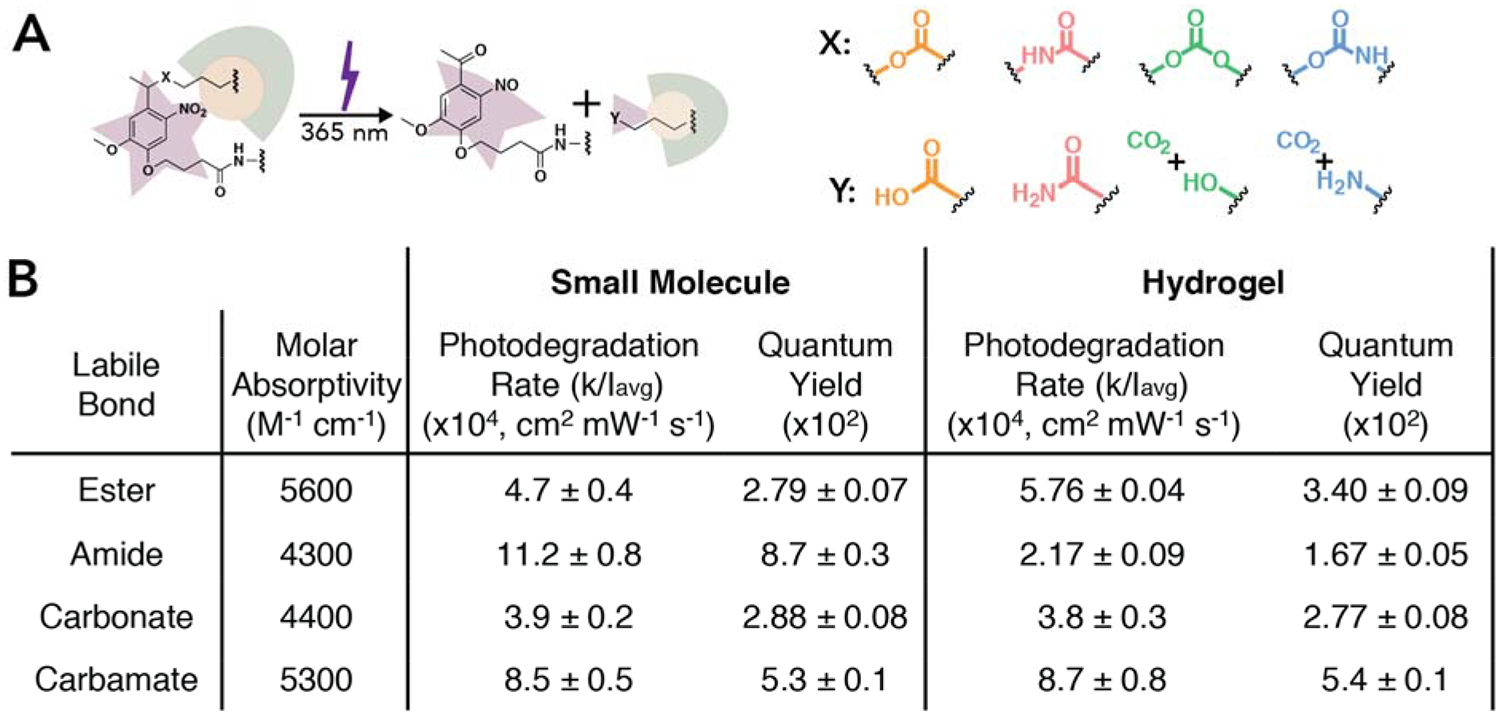
(A) The NB moiety incorporated within the hydrogel backbone undergoes a β-elimination reaction upon 365 nm light irradiation. Four different photocleavable bonds, X, were investigated, all of which lead to different cleavage products, Y (as confirmed by NMR and mass spectrometry, Figure S21 – S24 and Table S1 – S4). (B) Small molecule NBs (I0 = 10 mW cm−2 resulting in an Iavg = 7.8 mW cm−2) and photolabile hydrogels (I0 = 4 mW cm−2 resulting in an Iavg = 3.9 mW cm−2) were irradiated with 365 nm light to determine the first order photodegradation rate and quantum yield. The molar absorptivity was determined using the absorbance of each small molecule NB moiety at 365 nm. First order rate constants were determined for each of the four NB groups with different cleavable bonds in solution and within hydrogels (Figure S20 and S27) and used to calculate the quantum yield. All formulations (NB-ester vs. NB-amide vs. NB-carbonate vs. NB-carbamate) were found to be statistically different except that determined for the NB-ester and NB-carbonate in solution and for the amide and carbonate in hydrogels (p = 0.05). For full statistical analysis see Tables S5, S7, and S8. The data shown illustrate the mean (n = 3) with error representing standard error.
