Figure 5.
Chlamydomonas VFL3 Protein Localizes to Basal Bodies and the Proximal Ends of Flagella
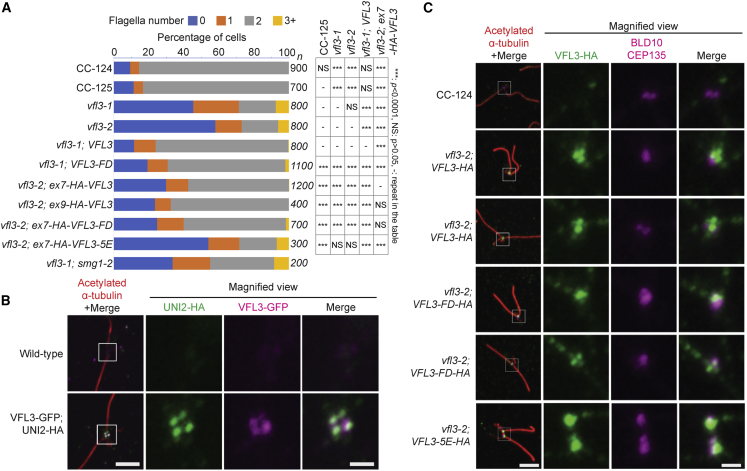
(A) Rescue of abnormal flagella numbers in vfl3 strains by wild-type VFL3. Bar chart showing flagella numbers observed in wild-type strains (CC-124 and CC125), mutant strains (vfl3-1 and vfl3-2), and the vfl3-1 and vfl3-2 strains expressing VFL3 constructs in Chlamydomonas. The numbers of cells “n” used for calculating ratio flagella numbers are shown on the right side of the chart. A χ2 test was used to determine if the number of cells with zero flagella was significantly different. NS, not significant; ∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
(B) Wild-type VFL3 protein localizes to Chlamydomonas basal bodies. In the first column, cells were stained with acetylated α-tubulin (red) for cilia and rootlet microtubules, anti-HA (green) for UNI2, and anti-GFP (magenta) for VFL3. Scale bar, 4 μm. Magnified views (4×) of the basal body regions (white boxes) are shown on the other three columns. Scale bars, 1 μm.
(C) Localization of VFL3 is affected in the 5E mutant. In the first column, cells were stained with acetylated α-tubulin (red) for cilia and rootlet microtubules, anti-HA (green) for wild-type and mutant VFL3, and anti-BLD10/CEP135 (magenta). Scale bar, 4 μm. Magnified views (4×) of the basal body regions (white boxes) are shown on the other three columns. Scale bar, 1 μm.
See also Figure S6.