Figure 2.
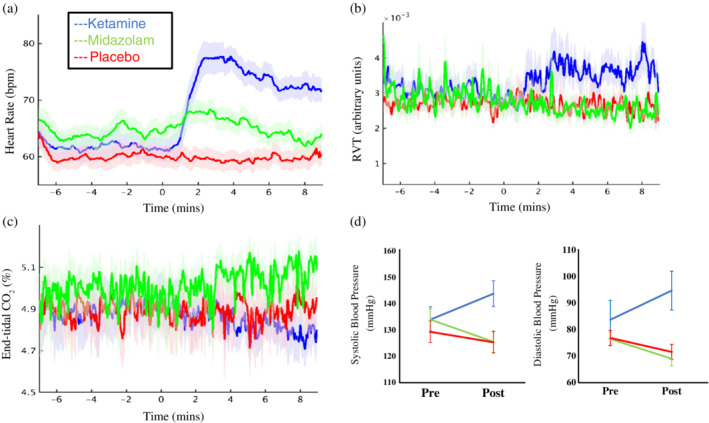
Changes in physiological measures. Depicted are the changes across time in heart rate (a), respiratory volume over time (b), and end‐tidal CO2, and the change in blood pressure between pre‐ and post‐drug, for placebo (red), ketamine (blue), and midazolam (green). Infusion started at time 0, and error bars/shading are the standard error of the mean. Only ketamine significantly modulated the first three parameters, with increases in HR (p < .001) and RVT (p = .04), and decreases in end‐tidal CO2 (p = .003). Ketamine also significantly increased both systolic (p = .01) and diastolic (p = .002) blood pressure, while midazolam decreased these (systolic: p < .001, diastolic: p = .005)
