Figure 1.
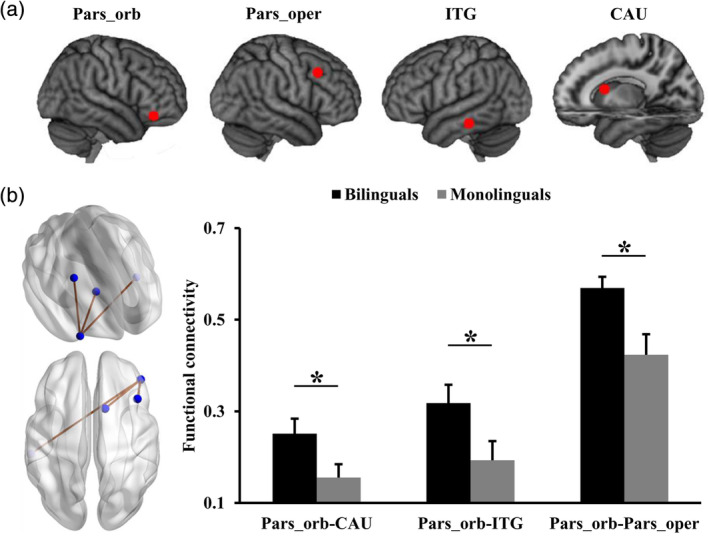
Differences in functional connectivities within language network between bilinguals and monolinguals. (a) Brain areas within language network showed changed functional connectivities in bilinguals compared to monolinguals. (b) Significantly increased functional connections of right pars‐orbital part of IFG (Pars‐orb) with right caudate (CAU), right pars‐opercular part of IFG (Pars‐oper), and left inferior temporal gyrus (ITG) in bilinguals compared to monolinguals
