Figure 5.
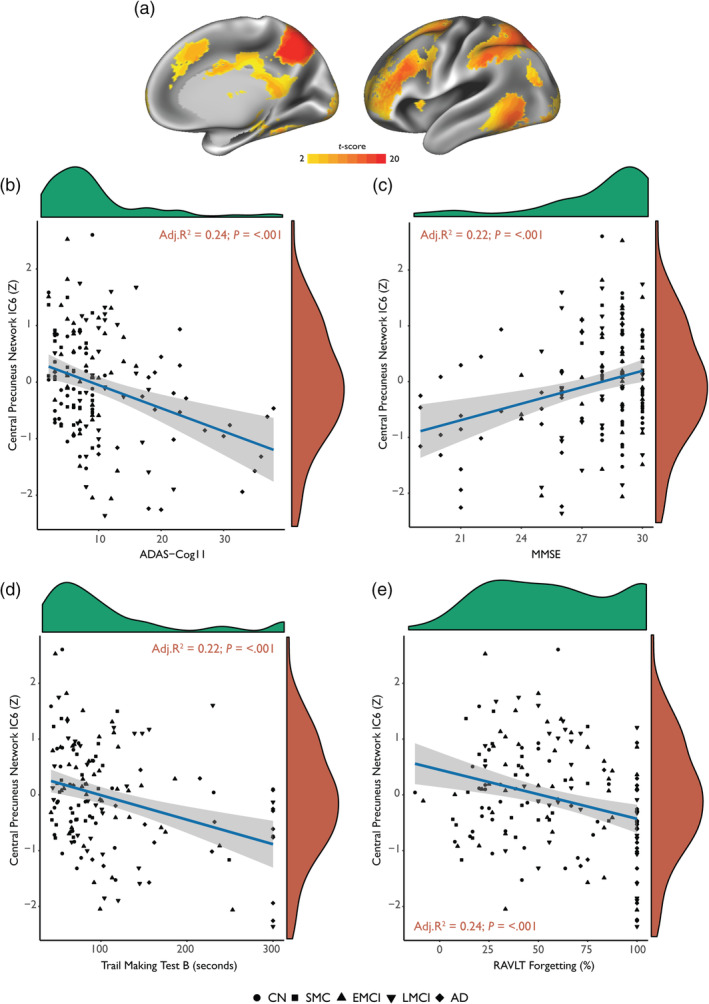
Functional connectivity of the central precuneus brain network is related to memory deficits and executive dysfunction across the Alzheimer's disease spectrum (N = 155). (a) Spatial map of the central precuneus “cognitive/associative” whole‐brain network is displayed on left lateral and right medial hemispheres. Functional connectivity of this network is plotted against (b) the 11‐item Alzheimer's disease assessment scale‐cognitive subscale (ADAS‐cog11) scores, (c) mini‐mental‐state examination (MMSE) scores, (d) trail making test B scores and (e) Rey auditory verbal learning test (RAVLT) forgetting scores expressed as percentages. The density distribution as marginal plots are displayed for cognitive variables in green and functional connectivity Z‐scores in red. Regression lines are shown in blue with 95% CIs (grey bands). Results displayed inset are from linear regression models. Age, gender, years of education and APOE ε4 genotype were considered as covariates in a stepwise fashion using Akaike Information Criterion minimisation. CN, cognitively normal; SMC, subjective memory complaints; EMCI, early mild cognitive impairment; LMCI, late mild cognitive impairment; AD, Alzheimer's disease
