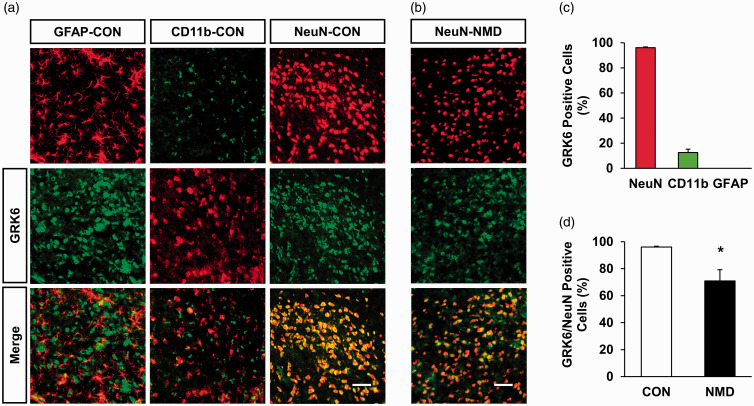
Figure 2.
NMD reduced the percentage of GRK6-positive ARC neurons. (a) GRK6-positive cells (middle) were co-labeled with the NeuN-positive cells (upper right, red). It was co-expressed with CD11b-positive cells (upper middle, green) in a small amount but not with GFAP-positive cells (upper left, red) in the ARC of CON rats. Scale bar = 50 µm. (b) GRK6-positive cells (middle, green) were co-labeled with the NeuN-positive cells (upper, red) in the ARC of NMD rats. Scale bar = 50 µm. (c) Data analysis showed that GRK6 was mainly present in NeuN-labeled neurons, a small amount in CD11b-labeled microglial cells, and not in GFAP-labeled astrocytes in ARC. (d) Statistic analysis indicated that GRK6-positive cells of NeuN in the ARC region of NMD rats was significantly decreased when compared with the CON rats (n = 3 for each group, *p < 0.05, two-tailed two-sample t-test). GFAP: glial fibrillary acidic protein; CON: control; NMD: neonatal maternal deprivation; NeuN: neuronal nuclei; GRK6: G protein-coupled kinase 6.