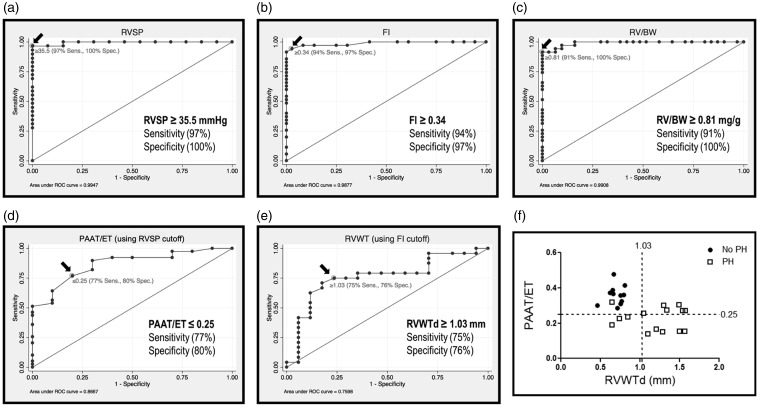
Fig. 4.
Invasive and non-invasive measures of pulmonary hemodynamics and RVH predict PH. (a) Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of RVSP. Arrow reflects the cutoff value of ≥35.5 mmHg as distinguishing between normal (normoxic) and pulmonary hypertensive rats with 97% sensitivity and 100% specificity (AUC = 0.9947). (b) ROC curve of Fulton's Index showing the sensitivity and specificity of FI to distinguish between normoxic and PH rats. The cutoff of ≥0.34 distinguishes PH with 94% sensitivity and 97% specificity (AUC = 0.9877). (c) ROC curve showing the sensitivity and specificity of RV/BW to distinguish between normal (normoxic) and PH rats. The cutoff of ≥0.81 mg/g distinguishes pulmonary hypertension with 91% sensitivity and 100% specificity (AUC = 0.9908). (d) ROC curve of PAAT/ET measurement accuracy as an indicator of RVSP ≥ 35.5 mmHg. Cutoff value of ≤0.25 predicts PH with 77% sensitivity and 80% specificity (AUC = 0.8667). (e) ROC curve of RVWTd accuracy in predicting a FI ≥ 0.34. The indicated cutoff value of RVWTd ≥ 1.03 predicts a FI ≥ 0.34 with 75% sensitivity and 76% specificity (AUC = 0.7598). (f) Correlation between PAAT/ET and RVWTd, showing the diagnostic thresholds for PH. Circles reflect animals without PH (RVSP < 35.5 mmHg and/or FI < 0.34), squares represent animals with PH (RVSP ≥ 35.5 mmHg and/or FI ≥ 0.34) (88% sensitivity and 100% specificity when either PAAT/ET ≤ 0.25 and/or RVWTd ≥ 1.03). Each data point represents one animal and dashed lines reflect threshold values.
RVSP: right ventricular systolic pressure; ROC: receiver operating characteristic; FI: Fulton's Index; RV: right ventricle; RV/BW: right ventricle to body weight ratio; PAAT/ET: pulmonary arterial acceleration time/ejection time; RVWTd: right ventricular wall thickness in diastole.