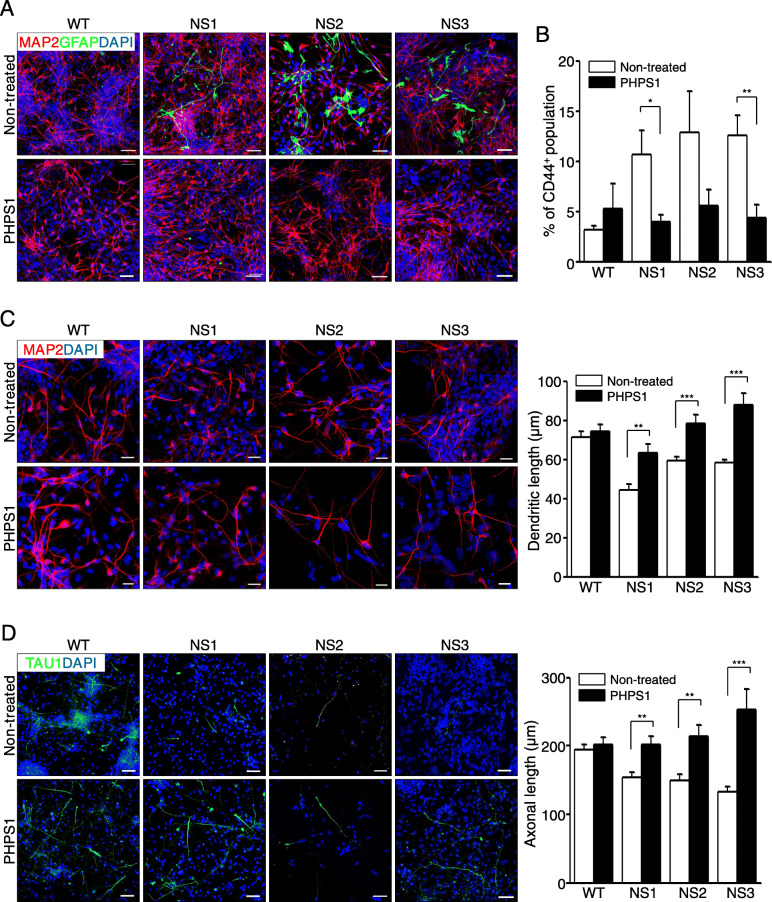
Fig. 4.
Recovery of abnormal phenotypes in the NS-neural cells by inhibition of SHP2 signaling. a Effects of SHP2 inhibition on gliogenesis in the NS-neural cells. WT-NPCs and NS-NPCs were treated with a SHP2 inhibitor (10 μM PHPS1) for 1 week and then differentiated into neural cells for 21–23 days. NS-neural cells treated with the inhibitor exhibited a lower proportion of GFAP-positive cells compared with the non-treated NS-neural cells. Scale bars, 50 μm. b Reduction of CD44+ population by SHP2 inhibition in the NS-neural cells. Percentages of CD 44+ population are expressed as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). c Extension of dendritic lengths in the NS-neural cells by SHP2 inhibition. Dendritic lengths were measured in the MAP2-positive cells of the WT- and NS-neural cells after treatment with the appropriate chemicals (n = 30 cells). The comparisons were analyzed against the results of three independent experiments. Scale bar, 20 μm. d Extension of axonal lengths in the NS-neural cells by SHP2 inhibition. Axonal lengths were measured in the TAU1-positive cells of the WT- and NS-neural cells after treatment with the appropriate chemicals (n = 30 cells). The comparisons were analyzed against the results from three independent experiments. Scale bar, 50 μm. p values were determined using an unpaired Student’s t test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Abbreviation: WT, wild-type; NS, Noonan syndrome; PHPS1, phenylhydrazonopyrazolone sulfonate 1