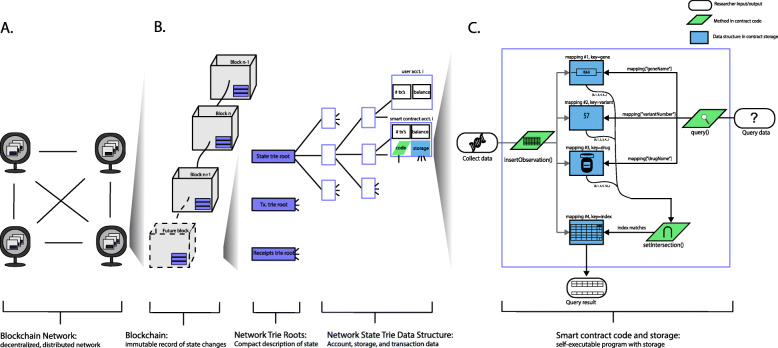
Fig. 1.
Ethereum blockchain and smart contracts. a A blockchain network consists of a decentralized, distributed digital ledger shared in a peer-to-peer fashion. The network schematic shown here contains four nodes (computers), each syncing a copy of the chain. The network is decentralized (there is no central point of control) and distributed (the chain is stored in multiple physical locations). b A blockchain can be visualized as a string of blocks linked by cryptographic hashes. That is, each block’s contents include the hash of the previous block’s contents. Blocks also contain data about the state of the network stored in a trie root. The state trie data structure in Ethereum stores information for user and smart contract accounts. c The code for a particular smart contract is housed at an address in network storage, and also maintains its own storage (for storing variables, for example). Here we show a flowchart depicting the insertion and query algorithms in our challenge solution smart contract