Figure 1. The Proteostasis Network.
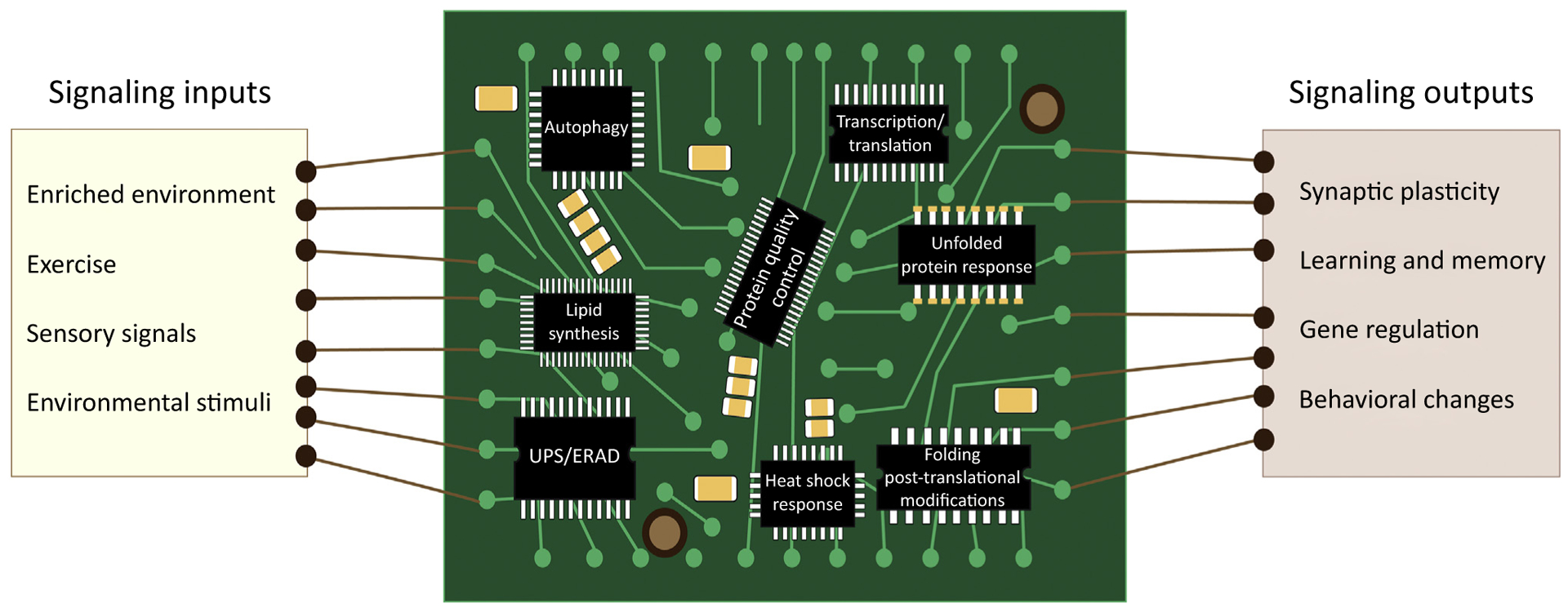
Several signaling inputs such as environmental enrichment, exercise, and various sensory signals induce changes in the brain proteostasis network, where the healthy brain adapts to these proteostatic perturbations, and facilitate resulting changes in gene expression that induce synaptic plasticity, learning, memory, and behavioral changes. The proteostasis network includes the autophagy pathway, the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated degradation machinery (ERAD), the unfolded protein response (UPR), the heat shock response (HSR), the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS), and mechanisms to improve protein quality control, transcription, translation, folding, post-translational modifications, lipid synthesis, chaperones, and foldases to re-establish homeostasis and maintain neuronal cell function.
