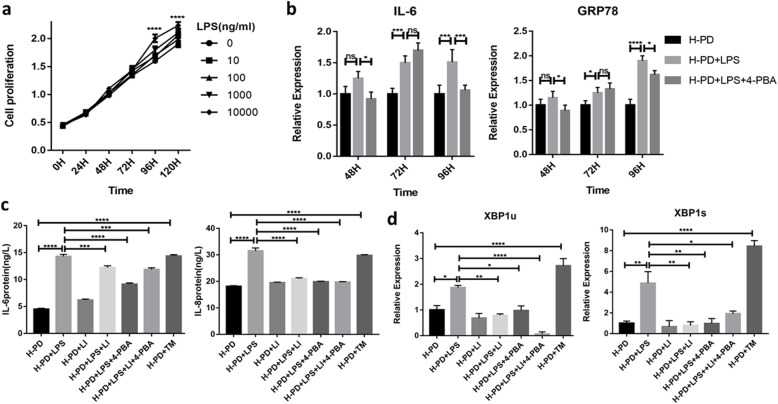
Fig. 5.
LPS induction simulated inflammatory microenvironment and LIPUS reduced inflammation by reducing UPR. a CCK-8 detected the proliferation of H-PDLSCs treated with LPS (0–10,000 ng/ml) and optimized the concentration of LPS (n = 5). b LPS and 4-PBA treated for different times, and the expression of ER and inflammation-related genes GRP78 and IL-6 were detected by qRT-PCR (n = 3). c ELISA detected the effects of LIPUS on inflammation-related genes (IL-6, IL-8) of H-PDLSCs induced by LPS (n = 3). d The expression of ERS-related genes XBP1u and XBP1s by qRT-PCR (n = 3). All data are presented as means ± SD. The representative results were from three independent experiments (*p < 0 .05; **p < 0 .01; ***p < 0 .001; ****p < 0 .0001). P-PD, P-PDLSCs; H-PD, H-PDLSCs; LI, LIPUS; H, hour