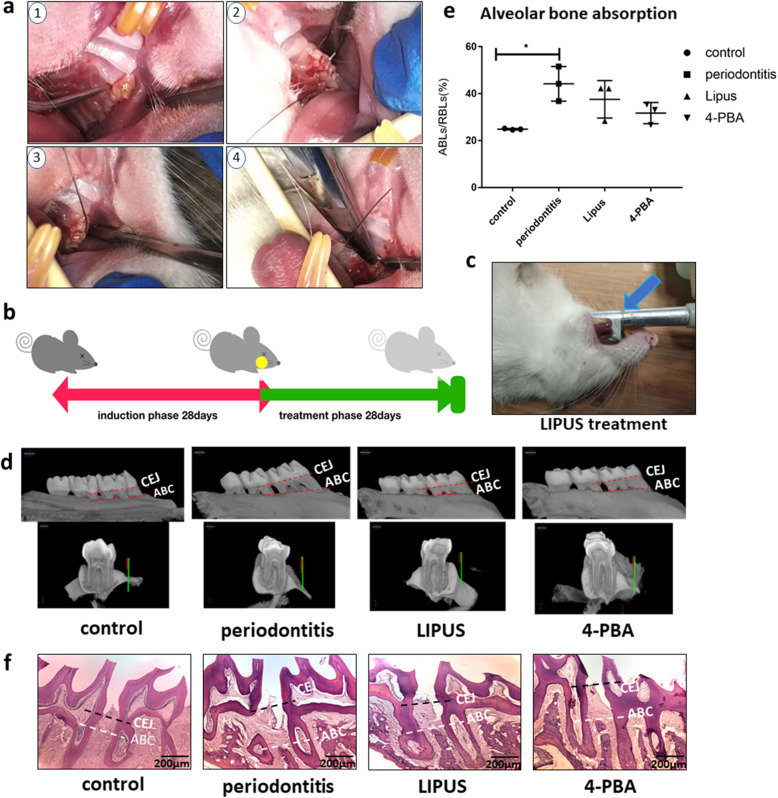
Fig. 7.
LIPUS and 4-PBA decreased alveolar bone absorption in experimental periodontitis in rats. a 4-step surgery procedures including separating the connective gingiva, ringing the ligature wire of the first maxillary molar, fastening the ligature, and ensuring the tight touch to the teeth to induce the experimental periodontitis in rats. b Schematic of 2 phases of the experimental periodontitis induction and treatment. c Picture of the LIPUS treatment in rat’s oral. The blue arrow is the ultrasonic probe of the LIPUS. d, f The alveolar bone absorption of SD rats (n = 3) was determined by micro-CT (d) and H&E staining (f). e The quantity results of the micro-CT, the absorption of the alveolar bone ratio (ABLs/RBLs) variable is used. The results of micro-CT and H&E staining showed less alveolar bone loss in both the LIPUS and 4-PBA treatment groups compared with the periodontitis group. Guide line CEJ means the parallel line of cemento-enamel junction (CEJ), and guide line ABC means the parallel line of alveolar bone Climax. The representative results were from three independent experiments. The error bars represent the S.D. from the mean values. *p < 0 .05; **p < 0 .01; ***p < 0 .001; ****p < 0 .0001