Fig. 6.
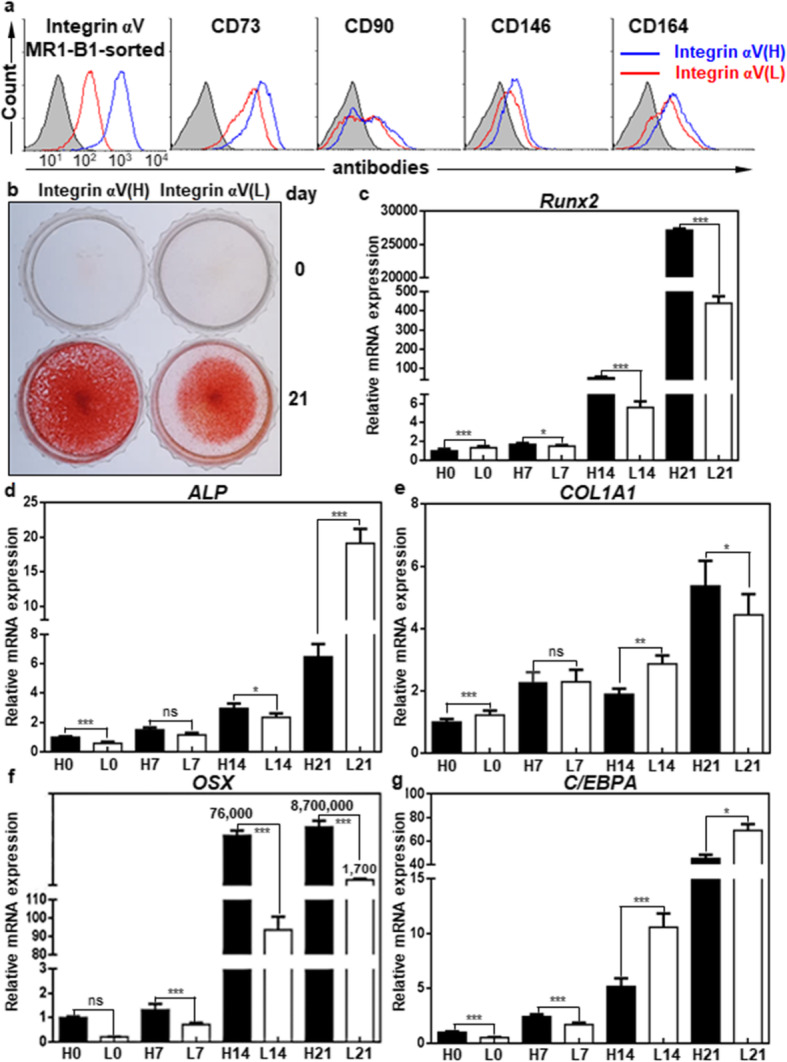
Integrin αV-high hMSCs have a greater osteogenic potential than integrin αV-low hMSCs. a Flow cytometric analysis of hMSCs with MR1-B1, anti-CD73, anti-CD90, anti-CD146, and anti-CD164 antibodies in integrin αV-high and αV-low hMSCs after MR1-B1-based magnetic cell sorting. b Alizarin Red S staining of OBs in integrin αV-high and αV-low hMSCs after being cultured in ODM for 21 days. To inhibit TGF-β1 signaling that originated from the culture medium, SB431542 was added to ODM after 7 days of osteogenic differentiation. Calcium deposition was visualized as red color after the cells were stained with Alizarin Red S. c–g Expression changes of osteogenic and adipogenic markers during osteogenic differentiation of hMSCs. Osteogenic markers (Runx2, ALP, COL1A1, OSX) and adipogenic marker (C/EBPA) were analyzed at 0, 7, 14, and 21 days of osteogenic differentiation in integrin αV-high (H0, H7, H14, H21) and αV-low (L0, L7, L14, L21) hMSCs by quantitative PCR. Values are depicted as a mean fold change in gene expression (2−ΔΔCT) of differentiated hMSCs at the indicated days compared to integrin αV-high hMSCs at day 0 (H0). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.005; ns, not significant
