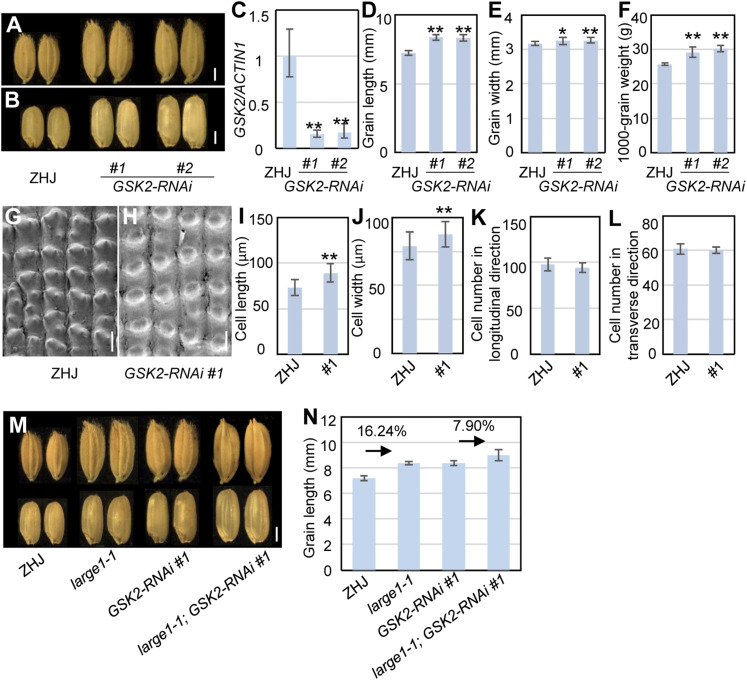
Figure 7.
GSK2 Acts Genetically with OML4 to Regulate Seed Size.
(A) Mature paddy grains of ZHJ and GSK2-RNAi.
(B) Brown rice grains of ZHJ and GSK2-RNAi.
(C) Expression level of GSK2 in ZHJ and GSK2-RNAi transgenic lines. RT-qPCR was used to measure expression levels of GSK2. Three biological replicates were used (n = 3). ACTIN1 was used to normalize expression.
(D) and (E) Grain length (D) and width (E) of ZHJ and GSK2-RNAi transgenic lines.
(F) The 1000-grain weight of ZHJ and GSK2-RNAi transgenic lines.
(G) and (H) Scanning electron microscopy analysis of the outer surface of ZHJ (G) and GSK2-RNAi #1 (H) lemmas.
(I) and (J) Average length (I) and width (J) of outer epidermal cells in the longitudinal direction in ZHJ and GSK2-RNAi #1 lemmas.
(K) and (L) Number of outer epidermal cells in the longitudinal (K) and transverse (L) direction in ZHJ and GSK2-RNAi #1 lemmas.
(M) Grains of ZHJ, large1-1, GSK2-RNAi#1, and large1-1; GSK2-RNAi#1.
(N) Grain length of ZHJ, large1-1, GSK2-RNAi#1 and large1-1; GSK2-RNAi#1.
Values ([D] to [F], [I] to [L], and [N]) are given as the means ± sd (n ≥ 50). *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 compared with the wild type by Student’s t test.
Bar in (A), (B), and (M) = 2 mm; bar in (G) and (H) = 50 µm.