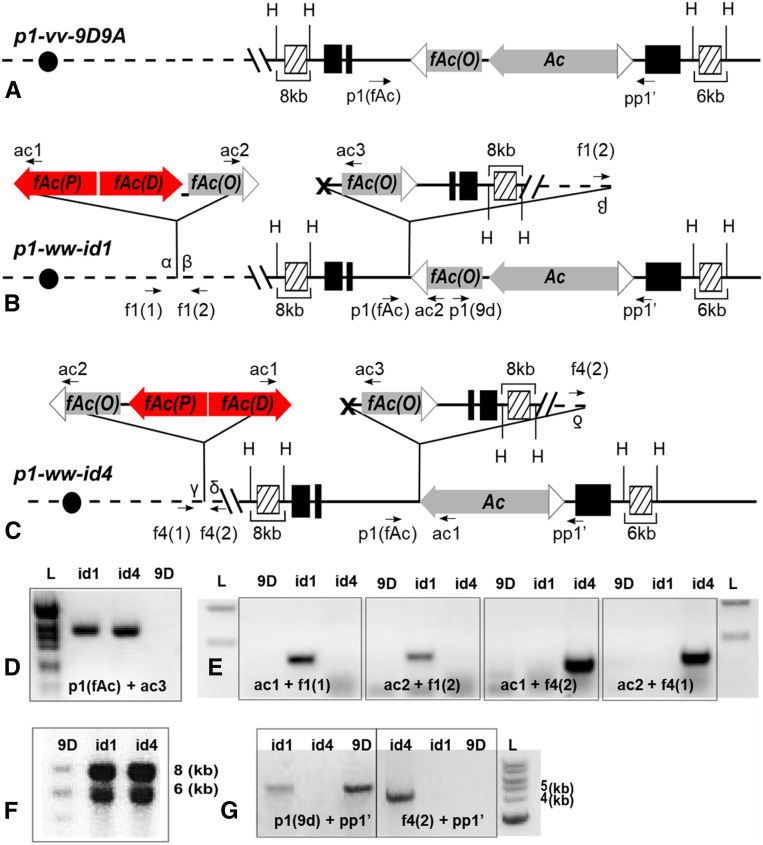
Figure 2.
p1-ww-id1 and p1-ww-id4 contain Composite Insertions and inverted duplications. (A–C) Structure of the progenitor allele p1-vv-9D9A (A), and expected structures of p1-ww-id1 (B) and p1-ww-id4 (C) based on the model of sister chromatid transposition-induced DNA rereplication. PCR primers are labeled as arrows, and sequences homologous to hybridization probe 15 are labeled as hatched boxes. H stands for HindIII restriction site. Other symbols are as in Figure 1. (D) Gel analysis of PCR to amplify the sister chromatid transposition footprints in p1-ww-id1 and p1-ww-id4. Bands were excised from the gel and sequenced (File S1). (E) Gel analysis of PCR to amplify the sequences flanking Composite Insertions. Bands were excised from the gel and sequenced to identify the target site duplications flanking each Composite Insertion (File S2). (F) Genomic Southern blot produced by digestion with HindIII and hybridization with probe 15. (G) Gel analysis of PCRs to determine the orientation of sister chromatid transposition (see text for details).