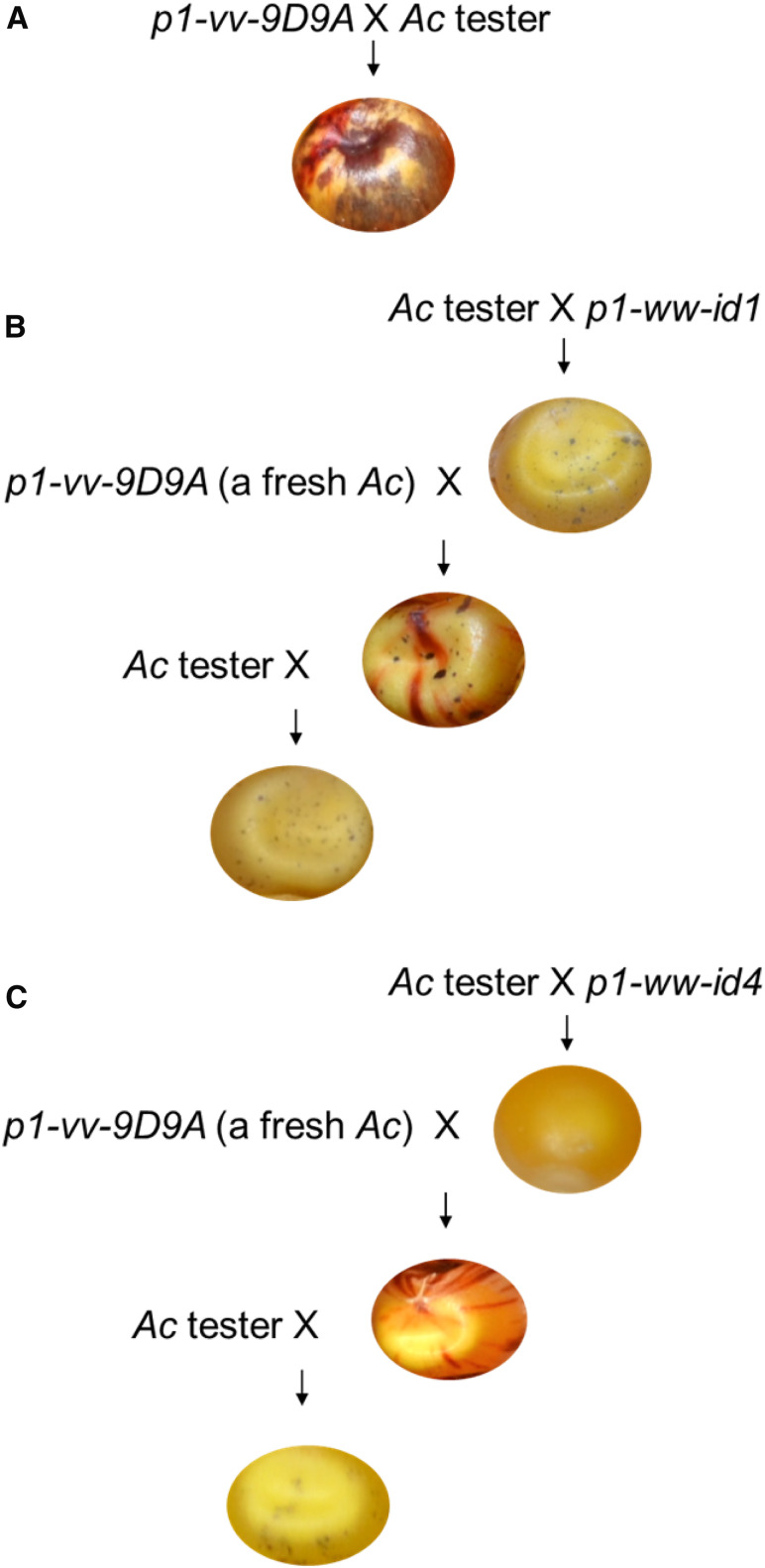
Figure 3.
Genetic crosses indicate the in-trans and heritable repression of Ac/Ds initiated by p1-ww-id1 and p1-ww-id4. (A) Progenitor allele p1-vv-9D9A contains a single active Ac element, shown by the heavily spotted kernel aleurone from the cross of p1-vv-9D9A and Ac tester. Cross: p1-vv-9D9A x r1-m3::Ds. (B) Ac activity is repressed in p1-ww-id1, shown by the fine spots in kernel aleurone in the first cross of p1-ww-id1 and Ac tester (p1-vv-id1 x r1-m3::Ds). The second cross (p1-vv-9D9A x p1-ww-id1) introduces a fresh active Ac in p1-vv-9D9A, which is repressed in trans by p1-ww-id1 (indicated by small aleurone spots). The third cross (r1-m3::Ds x p1-vv-9D9A/p1-ww-id1) shows that silencing of Ac in p1-vv-9D9A is heritable, as small spots are maintained even after p1-vv-9D9A is segregated from p1-ww-id1. (C) Parallel crosses of p1-ww-id4 as in B. Ac activity is repressed in the line of p1-ww-id4, shown as absence of kernel aleurone spots in the first cross between p1-ww-id4 and Ac tester. The repression is trans-dominant, shown by the absence of spots in kernels produced by cross of active Ac from p1-vv-9D9A by p1-ww-id4. Ac repression is heritable, shown by the fine spotting in kernels from the third cross in which p1-vv-9D9A is segregated from p1-ww-id4.