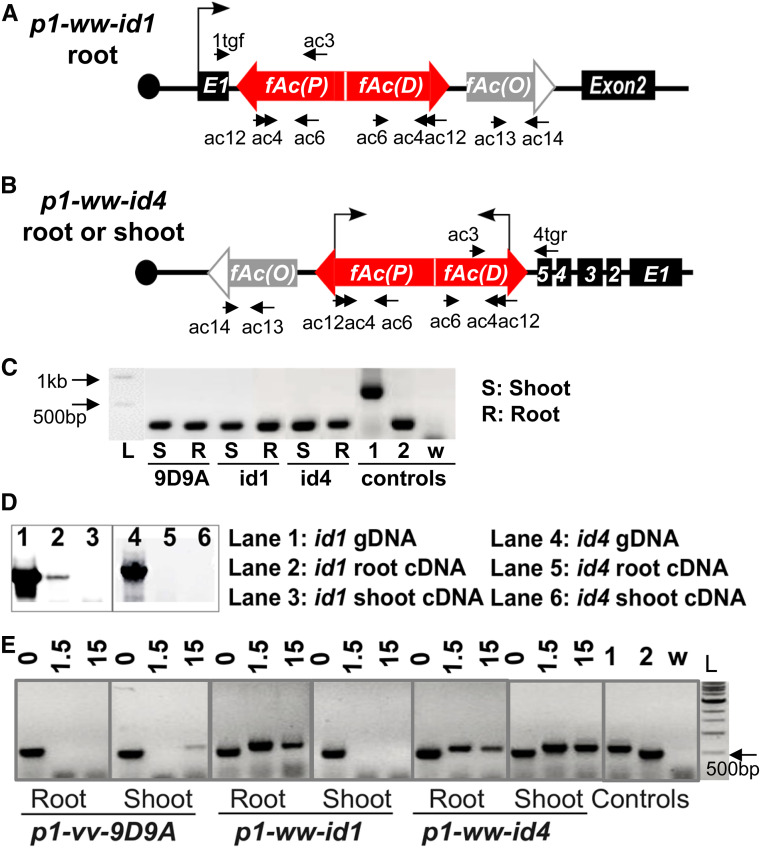
Figure 6.
Composite Insertions in p1-ww-id1 and p1-ww-id4 produce dsRNA transcripts. (A) Structure of the Composite Insertion in p1-ww-id1, located in intron 1 of gene Zm00001d028930. Bent arrow indicates transcription from the host gene promoter to generate read-through transcripts of the Composite Insertion in root tissues, but not shoot. Labeled arrows indicate primers used in RT-PCR. (B) Structure of the Composite Insertion in p1-ww-id4, located in intron 5 of Zm00001d028863. The promoter of Zm00001d028863 is not active in either root or shoot tissues. Bent arrows indicate transcription from the native Ac promoters. (C) Test of genomic DNA contamination in RNA samples. Primers ac13 + ac14 are located in fAc(O) outside the dsRNA region, in Ac exons 3 and 5 (Figure 6, A and B). Bands of 744 bp and 272 bp are expected from genomic DNA and spliced cDNA, respectively. Control lanes “1” and “2” are from templates of genomic DNA and root cDNA, respectively, of p1-ww-id1; lane “w” is from a water template as a control for PCR contamination. (D) Test for chimeric transcripts by RT-PCR using primers 1tgf + ac3 in p1-ww-id1 (lanes 1–3), and 4tgr + ac3 in p1-ww-id4 (lanes 4–6). Chimeric transcript initiating from flanking gene promoter was detected only in p1-ww-id1 root. No chimeric transcript from flanking gene promoter was detected in p1-ww-id4. (E) Detection of dsRNA by RNase protection assay. Total RNA from the indicated tissues and alleles were treated with DNase1 and three quantities of RNase A/T1 (0, 1.5, and 15 units). Treated RNA samples were then analyzed by a seminested PCR (primers ac12 + ac6; followed by ac4 + ac6). Control lanes “1” and “2” are from templates of genomic DNA and root cDNA, respectively, of p1-ww-id1; lane “w” is from a water template as a control for PCR contamination.