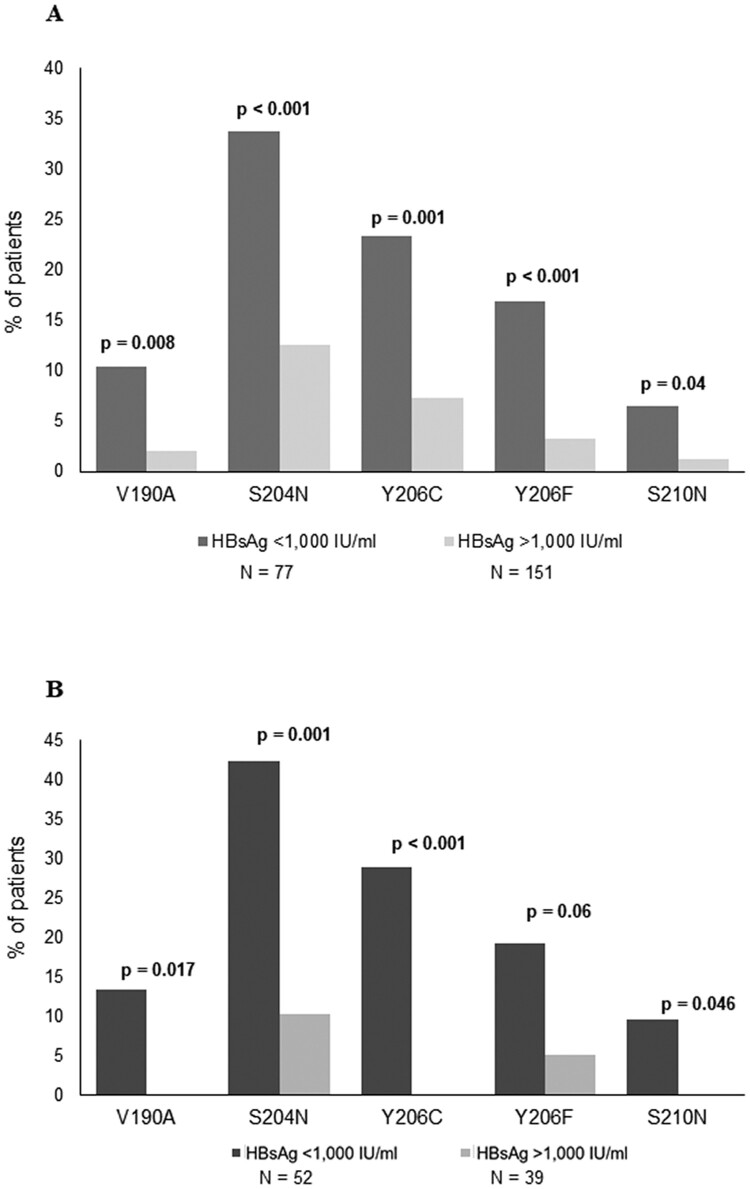
Figure 2.
Mutations in HBsAg C-terminus associated with HBsAg<1,000IU/ml. The prevalence of each mutation in HBsAg C-terminus (amino acids: 170-226) was calculated in 228 HBV genotype-D infected patients stratified according to HBsAg levels (N=77 with HBsAg <1,000IU/ml and N=151 with HBsAg >1,000IU/ml) (A) and in 91 patients with HBeAg-negative genotype-D infection (N=52 with HBsAg<1,000IU/ml and N=39 with HBsAg>1,000IU/ml) (B). Statistically significant differences were assessed by Fisher Exact Test. In (A) Benjamini-Hochberg Method was used for multiple comparison correction. Statistically significant differences were confirmed after correction for multiple comparison for all mutations with the exception of S210N.