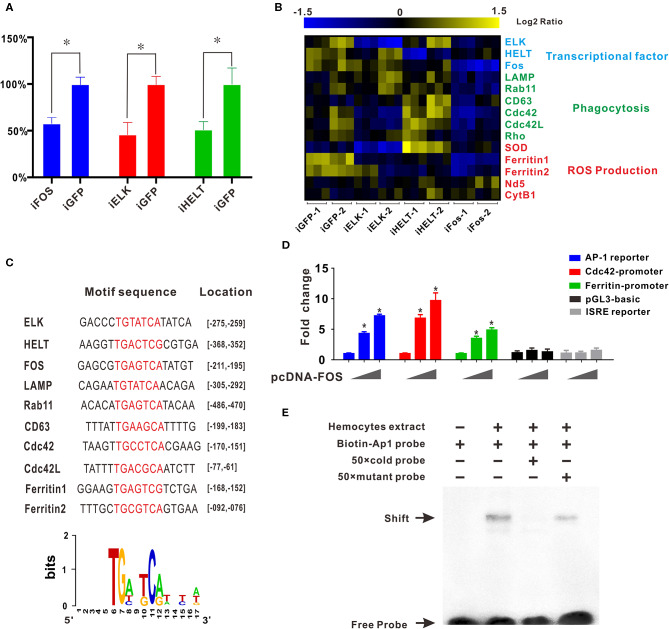
Figure 4.
Transcription factor Fos regulates transcriptional activation of granulocyte-specific genes. (A) Inhibition rate of RNA interference of three transcription factors (Fos, ELK, and HELT) in vivo. Blue panel, interference of Fos; red panel, interference of ELK; green panel, interference of HELT. (B) mRNA expression levels of immunity-related genes after knockdown of three transcription factors (ELK, HELT, and Fos). Detected genes were classified into three groups based on their potential functions: transcription factors, phagocytosis, and ROS production. Colors from yellow to blue indicate range of log2 ratio values (in descending order); yellow color indicates high expression level and blue color indicates low expression level. (C) Transcription factor binding site prediction software identified an AP-1 site that was highlighted in promoter element sequence of some immunity-related genes. Specific nucleotides were marked with red color. (D) Relative luciferase activity by expression of Fos plasmid for the luciferase reporter genes, AP-1 reporter Luc (blue panel), Cdc42 promoter reporter Luc (red panel), Cdc42l promoter reporter Luc (green panel), pGL3-basic vector (black panel), and ISRE-luc reporter (gray panel) in HEK293T cells. Plasmid pcDNA-Fos were added in gradient concentration (0, 150, and 300 ng). *p < 0.05. (E) AP-1 probe was labeled with biotin and incubated with C. gigas-extracted hemocyte proteins. Unlabeled specific competitor sequences (cold probe) were used in a 50-fold surplus over labeled target.