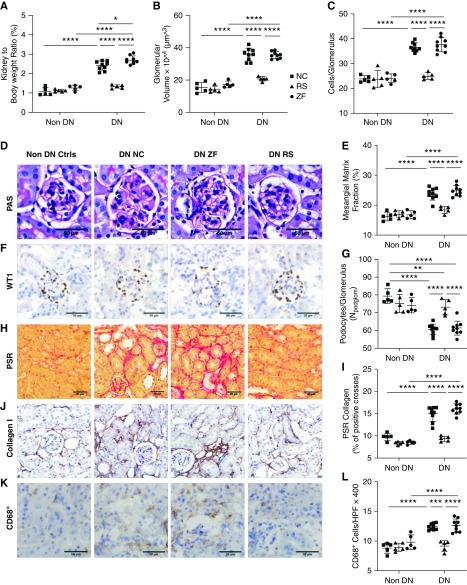
Figure 2.
RS feeding reduced glomerular and interstitial injury in DN. Diabetic mice fed RS are relatively protected from diabetes-induced glomerular and interstitial injury compared with NC- and ZF-fed mice, as indicated by (A) decreased kidney-to-body weight ratio, (B and D) VG, (C) glomerular hypercellularity, and (E) mesangial expansion. (D) Representative sections of glomeruli from NC-, ZF-, and RS-fed diabetic and NC-fed nondiabetic mice at 12 weeks (PAS-stained, ×400 magnification). (F and G) Representative sections of glomeruli stained for WT-1 at 12 weeks (×400 magnification), demonstrating podocyte density in nondiabetic mice, which is reduced in NC- and ZF-fed mice, with relative preservation in with RS feeding. Representative sections of kidney from diabetic and nondiabetic mice at 12 weeks demonstrating the increased interstitial collagen deposition being attenuated by RS feeding using (H and I) picrosirius red staining and immunostaining for (J) Col-I. (K) Representative sections of kidney from diabetic and nondiabetic mice stained for CD68. (L) Increased interstitial CD68+ macrophage accumulation is evident in diabetic NC- and ZF-fed, but not RS-fed mice. Data are shown as means±SD; *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001; ****P<0.0001.