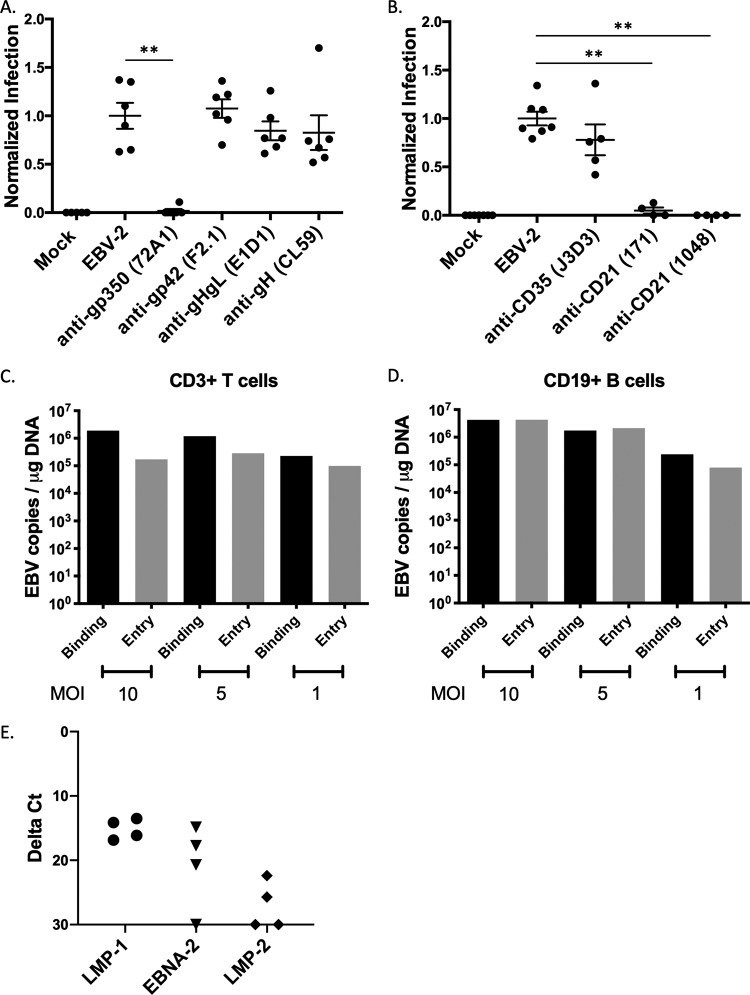
FIG 1.
Neutralization assay to assess viral glycoproteins and cellular receptors for EBV-2 infection of T cells. CD3+ T cells were infected with EBV incubated with antibodies to either EBV glycoproteins (A) or complement receptors (B). (A) Neutralization assay after incubation of virus with 10 μg monoclonal antibodies against EBV glycoproteins. Mock, uninfected cells; EBV-2, no antibody; anti-gp350, clone 72A1; anti-gp42, clone F2.1; anti-gHgL, clone E1D1; anti-gH, clone CL59. Viral loads were normalized to the uninhibited EBV-2 infection for each experiment and are presented as normalized infection. 72A1, P = 0.0022; F2.1, P = 0.6991; E1D1, P = 0.4610; CL59, P = 0.3939). (B) Neutralization assay with incubation of purified T cells with 20 μg monoclonal antibodies against CD35 (clone J3D3) or CD21 (clones 171 and 1048). Viral loads were normalized to infection with uninhibited EBV-2 infection (J3D3, P = 0.1174; 171, P = 0.0061; 1048, P = 0.0061). Infections were performed with 5 EBV genome copies/cell (n = 4 to 6). (C) CD3+ T cells were incubated with EBV-2 at different MOI for 1 h at 4°C (binding) or for 1 h at 4°C with a subsequent shift to 37°C (entry). Cells were analyzed for viral load by qPCR at 24 hpi. Data are from replicate wells. (D) CD19+ B cells were incubated with EBV-2 at different MOI for 1 h at 4°C (binding) or for 1 h at 4°C with a subsequent shift to 37°C (entry). Cells were analyzed for viral load by qPCR at 24 hpi. Data are from replicate wells. (E) CD3+ T cells were infected with EBV-2, and viral gene expression was analyzed by RT-PCR at 24 hpi. Data shown are from four replicates.