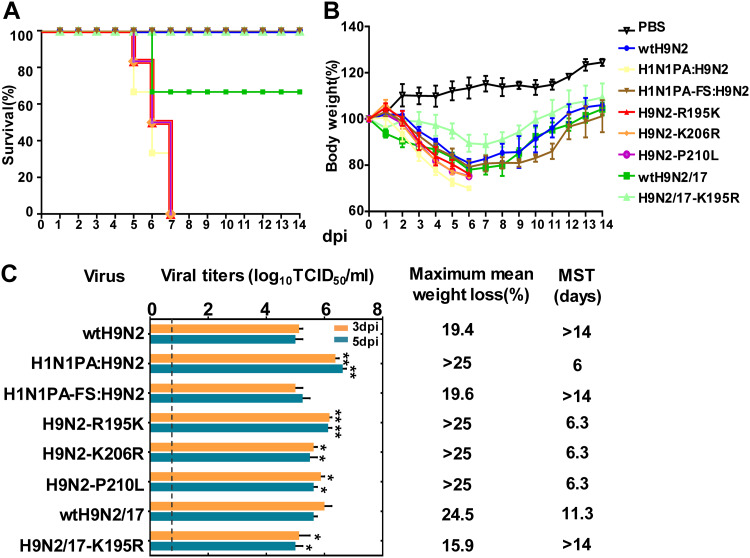
FIG 1.
Virulence of H9N2 viruses in mice. Mice were intranasally inoculated with 106 TCID50 of each test virus or with PBS. (A and B) The survival rates and body weights of six inoculated mice were measured and are represented as percentages of the weight on the day of inoculation (day 0). (C) Mean viral titers in the lungs of three mice. The error bars indicate standard deviations of the virus titers in the lungs. The dashed line indicates the lower limit of detection. Maximum mean weight loss (percent weight loss relative to 0 dpi) and the mean survival time (MST) are shown. Statistical significance relative to the corresponding wild-type H9N2 virus was assessed by two-way ANOVA (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01).