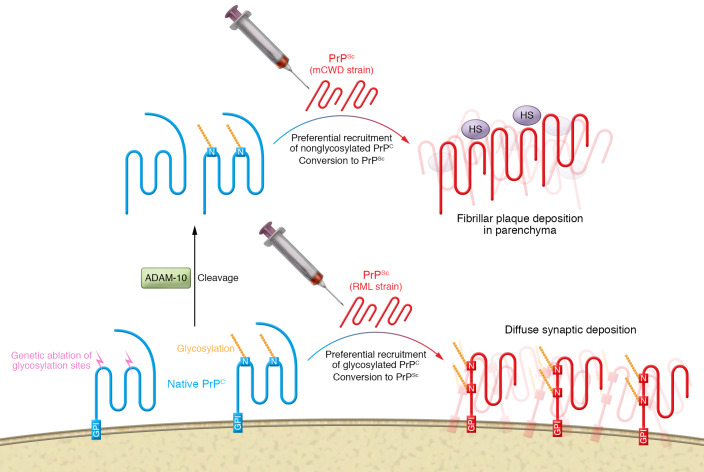
Figure 1. Role of posttranslational processing of PrPC in the formation of prion aggregates.
Fibrillar prion strains such as mCWD preferentially incorporate underglycosylated PrPC (blue) that is released from the cell surface by ADAM-10 into plaques that form in association with HS in the parenchyma. Subfibrillar prion stains, such as RML, preferentially incorporate glycosylated PrPC into diffuse synaptic deposits of PrPSc (red) without a HS scaffold. Genetic ablation of N-linked glycosylation sites (N) can switch in nonfibrillar strain pathology from synaptic diffuse deposition to plaque-like deposition of PrPSc in the parenchyma.