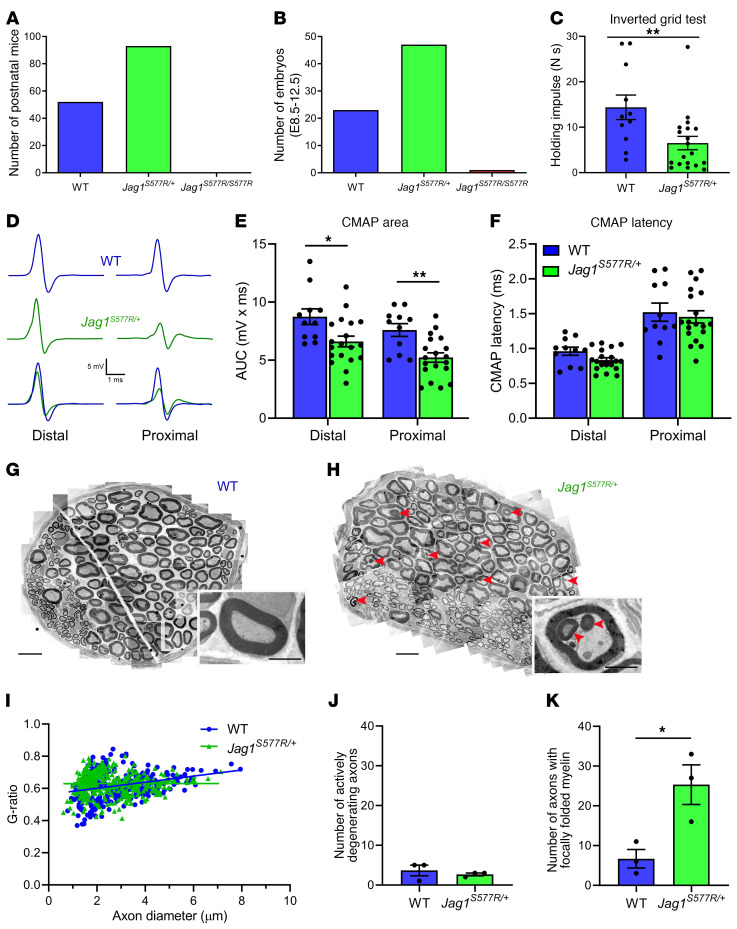
Figure 4. Homozygous expression of the JAG1S577R mutation causes embryonic lethality in mice, while heterozygous expression results in mild peripheral neuropathy.
(A and B) Genotyping of postnatal (A) and embryonic (B; E8.5–E12.5) mice generated from heterozygous intercrosses demonstrates embryonic lethality in Jag1S577R/S577R mice. (C–F) Jag1S577R/+ mice display impaired performance in the inverted grid test (C) as well as reductions in CMAP area (D and E), but not latency (F). Representative CMAP traces are shown in D. n = 11 for WT; n = 19 for Jag1S577R/+. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, 2-tailed Student’s t test. (G and H) TEM reconstructions of the recurrent laryngeal nerve of WT (G) and Jag1S577R/+ (H) mice. Insets show higher magnification images of individual myelinated axons. Scale bars: 10 μm; 2 μm (insets). Arrowheads indicate regions of focally folded myelin (15). (I–K) Myelinated axons in the recurrent laryngeal nerve of Jag1S577R/+ mice exhibit normal g-ratios (I) and numbers of actively degenerating axons (J), but an increased incidence of focally folded myelin (K) For I, n = 350 axons from 3 WT mice; n = 410 axons from 3 Jag1S577R/+ mice. For J and K, n = 3 for WT and Jag1S577R/+. *P < 0.05, 2-tailed Student’s t test.