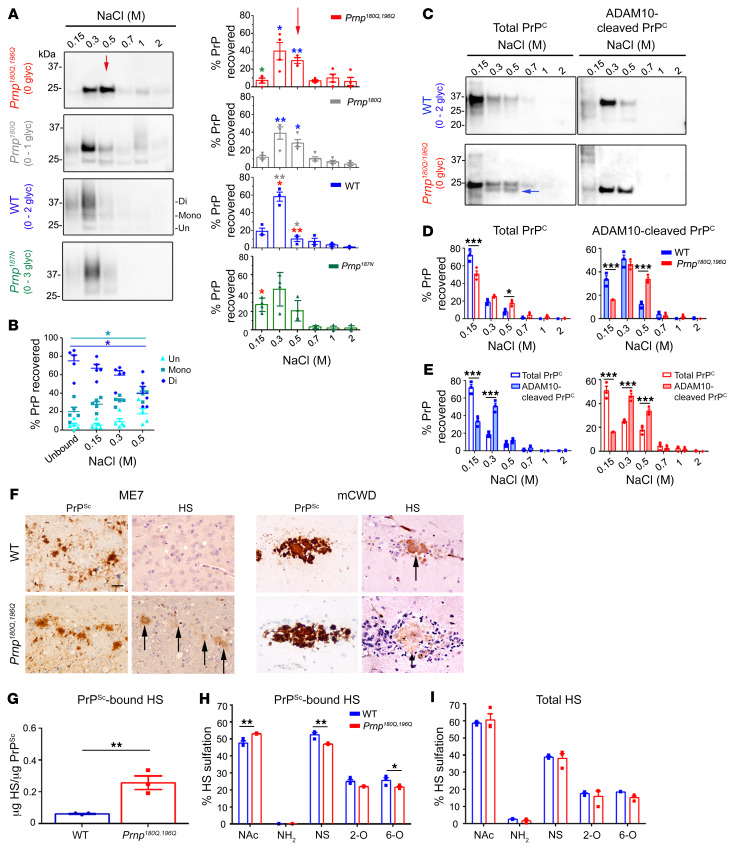
Figure 6. PrP glycans hinder binding to HS.
(A) Immunoblots of heparin affinity chromatography experiments assessing variably glycosylated PrP. Relative levels of PrP from each elution are shown in the graphs. Differences in the binding affinity are most notable in the 0.5 M NaCl elution (red arrow). Asterisk color indicates the mutants with significant differences. The triglycosylated PrP isoform level was low in RK13 cells; n = 3–4 experiments. (B) Among the WT PrP glycoforms, diglycosylated PrP has a lower heparin affinity than mono- or unglycosylated PrP (unbound is PrP in the flow-through); n = 5 experiments, 4 also included in A. (C) Affinity chromatography of the soluble brain fraction reveals that total and ADAM10-cleaved PrP180Q/196Q have significantly higher heparin affinity than the corresponding WT PrP. PrP180Q/196Q shows a second band (blue arrow) that corresponds to ADAM10-cleaved PrPC. (D) Quantification of PrP shown in C; n = 3/strain. (E) ADAM10-cleaved PrP has a higher heparin-binding affinity than total PrP for both WT PrP and PrP180Q/196Q. (F) Immunolabelling reveals HS colocalizes to ME7 plaques in the Prnp180Q/196Q brain only and to mCWD plaques in both the WT and Prnp180Q/196Q brain; n = 4/strain. Scale bar: 50 μm. (G) LC-MS reveals approximately 6-fold more HS bound to unglycosylated ME7 PrPSc than to highly glycosylated ME7 PrPSc (WT); n = 3/strain. (H) Composition analysis of HS bound to purified PrPSc (ME7) reveals less N-sulfated (NS) and 6-O sulfated (6-O) HS bound to unglycosylated (Prnp180Q/196Q) as compared with glycosylated (WT) PrPSc; n = 3/group. (I) The overall HS composition in ME7-infected Prnp180Q/196 and WT whole-brain lysates are similar; n = 3/group. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, and ***P ≤ 0.001; 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post hoc test (A, D, E, and H). *P < 0.05; 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s test (B). **P ≤ 0.01, unpaired, 2-tailed Student’s t test (G).