Fig. 2. Susceptibility of M. tuberculosis strains under various stress conditions and host tissues.
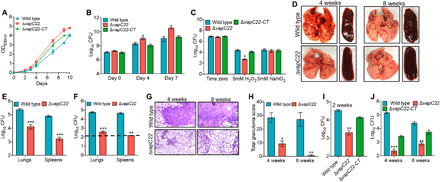
(A and B) In vitro growth curves of wild-type, ΔvapC22, and ΔvapC22-complemented strains in liquid cultures. The growth kinetics of parental, ΔvapC22, and ΔvapC22-complemented strains was performed in Middlebrook 7H9 medium by measuring either optical density at 600 nm (OD600nm) (A) or colony-forming unit (CFU) analysis (B) at regular intervals. (C) The effect of deletion of vapC22 on M. tuberculosis susceptibility upon exposure to oxidative and nitrosative stress. Early-log phase cultures of various strains were exposed to either oxidative or nitrosative stress. For bacterial enumeration, 10.0-fold serial dilutions were prepared, and 100 μl was plated on Middlebrook 7H11 medium at 37°C for 3 to 4 weeks. The results shown in these panels are means ± SE of data obtained from three independent experiments. Statistically significant differences were obtained for the indicated groups (paired two-tailed t test, *P < 0.05). (D to J) The effect of deletion of vapC22 on growth of M. tuberculosis in guinea pigs and immunocompetent mice. (D) The representative images of lung and spleen tissue from guinea pigs infected with either wild-type or ΔvapC22 strain via aerosol route are shown. Photo credit: Sakshi Agarwal, Translational Health Science and Technology Institute. (E and F) The bacterial loads were determined by plating lung and spleen homogenates at 4 weeks (E) and 8 weeks (F) after infection. The homogenates were serially diluted and plated on Middlebrook 7H11 medium at 37°C for 3 to 4 weeks. The data shown in these panels are means ± SE of log10 CFU obtained from either six or seven guinea pigs per group per time point. (G) Lung sections of guinea pigs infected with wild-type and ΔvapC22 strain were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and viewed at a magnification of ×40. Scale bars, 200 μm. Photo credit: Ashok Mukherjee, National Institute of Pathologist. (H) The total granuloma score in H&E-stained sections from wild-type and ΔvapC22-infected guinea pigs was determined as previously described. The data shown in means ± SE of total granuloma score obtained from six or seven animals per group. (I to J) Female Balb/c mice were infected with parental, ΔvapC22 mutant, and ΔvapC22-complemented strains via a low-dose aerosol infection. At 2 weeks (I), 4 weeks, and 8 weeks (J) after infection, lungs were homogenized, serially diluted, and plated to obtain bacterial loads. The data shown in panels B, C, E, F, H, I, and J are means ± SE of log10 CFU obtained from five animals per group per time point. Statistically significant differences were obtained for the indicated groups (paired two-tailed t test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001).
