Fig. 3. Disruption of hepatic vagal innervation prevents the metabolic deficits caused by HFD feeding of AgRP-barr1-KO mice.
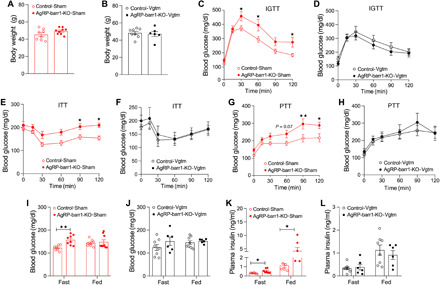
All experiments were carried out with male mice that had been maintained on an HFD for at least 8 weeks. Mice in which the vagal innervation of the liver had been disrupted are referred to as AgRP-barr1-KO-Vgtm and Control-Vgtm mice, respectively. Mice that had been subjected to sham surgery are referred to as AgRP-barr1-KO-Sham and Control-Sham mice, respectively. (A) Body weights of AgRP-barr1-KO-Sham and Control-Sham mice (age, 18 weeks; 8 weeks on HFD). (B) Body weights of AgRP-barr1-KO-Vgtm and Control-Vgtm mice (age, 18 weeks; 8 weeks on HFD). (C and D) Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (IGTT; 1 g glucose/kg i.p.) carried out with mice subjected to sham surgery (C) or vagotomy (D) (age, 18 weeks; 8 weeks on HFD). (E and F) Insulin tolerance test (1 U/kg i.p.) performed with mice subjected to sham surgery (E) or vagotomy (F) (age, 19 weeks; 9 weeks on HFD). (G and H) Pyruvate tolerance test (PTT; 2g/kg i.p.) carried out with mice subjected to sham surgery (G) or vagotomy (H) (age, 20 weeks; 10 weeks on HFD). (I and J) Fasting and fed blood glucose levels of sham-operated (I) or vagotomized (J) mice (age, 18 to 19 weeks; 8 to 9 weeks on HFD). (K and L) Fasting and fed plasma insulin levels of sham-operated (K) or vagotomized (L) mice (age, 18 to 19 weeks; 8 to 9 weeks on HFD). Data are given as means ± SEM (n = 6 to 9 male mice per group). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 [two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test (C, E, and G) and two-tailed Student’s t test (I and K)].
