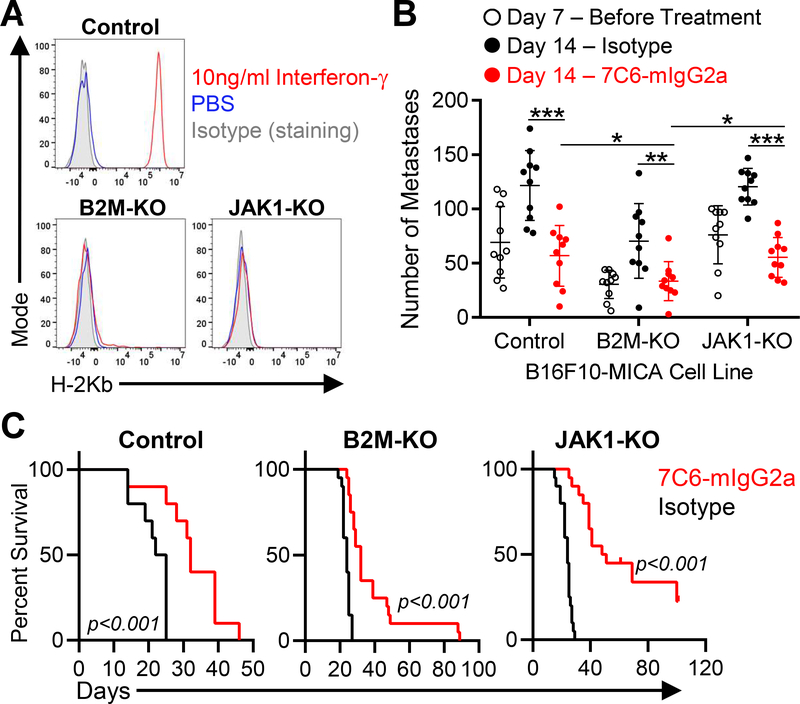
Figure 2. MICA/B mAb treatment induces immunity against melanoma metastases with inactivating mutations in B2m and Jak1 genes.
(A) B16F10-MICA cells (control, B2m-KO, or Jak1-KO) were treated for 24 hours with IFNγ (10 ng/mL) or solvent control (PBS), and subsequently surface level of H-2Kb was analyzed by flow cytometry. (B) MICA/B mAb treatment effects on established metastases with inactivating mutations in B2m or Jak1 genes. B16F10-MICA cells (7×105 control, B2m-KO or Jak1-KO tumor cells) were injected i.v. into B cell–deficient (Ighm–/–) mice. On day 7, a subset of mice was euthanized for quantification of metastases, while the remaining mice were treated with 7C6-mIgG2a or control mAbs (200 μg i.p. on days 7, 8, and 12). On day 14, lung surface metastases were counted under a stereomicroscope. Each dot represents one mouse and error bars indicate standard deviation (SD). (C) Impact of MICA/B mAb treatment on survival of mice with B2m or Jak1 deficient melanoma metastases. WT mice (Ighm+/+) were inoculated i.v. with 2 × 105 control, B2m-KO, or Jak1-KO B16F10-MICA cells. Mice received 7C6-mIgG2a or isotype control mAbs on days 1 and 2, and mouse survival was recorded. The number of mice per group is as follows: Control (n=10), B2m-KO (n=20), and Jak1-KO (n=20). Data representative of three independent experiments (A) or pooled from three (B) or two (C) independent experiments. Statistical analyses were performed by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-tests (B), and Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test (C). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.