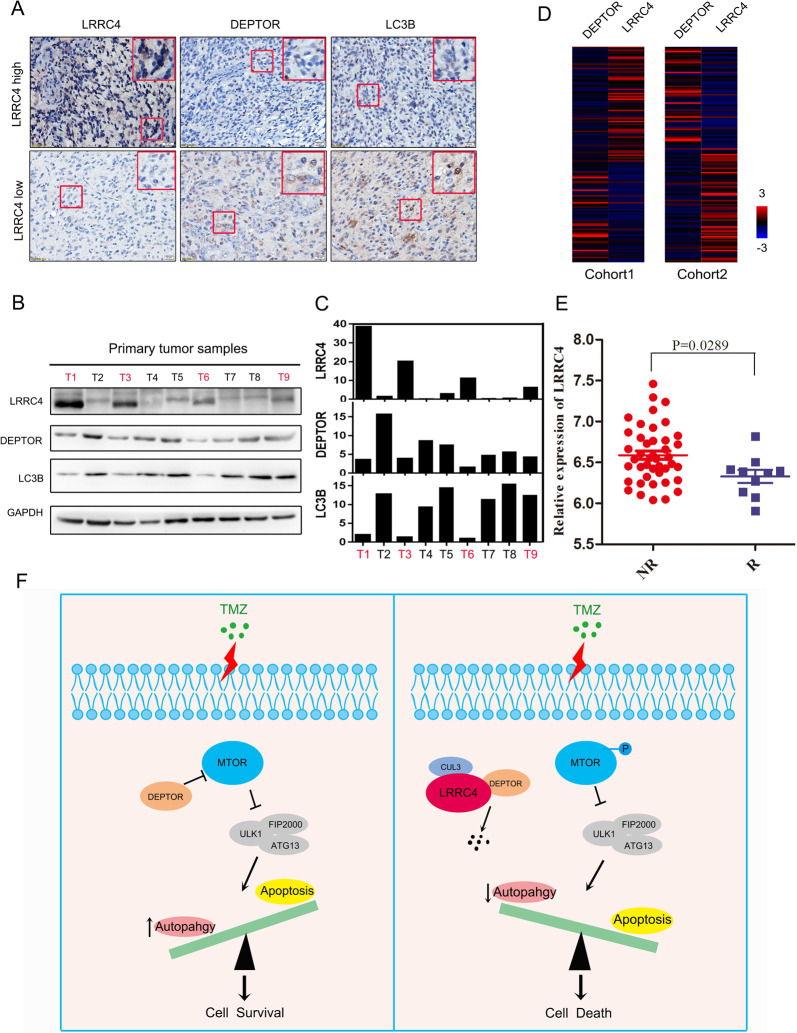
Fig. 8. The Levels of LRRC4, DEPTOR and LC3B are clinically relevant for GBM.
a Representative immunohistochemistry staining of LRRC4, DEPTOR and LC3B proteins in GBM tissues. (LRRC4 high GBM tissues = 5, LRRC4 low GBM tissues = 27). b Representative western blotting analysis of LRRC4, DEPTOR and LC3B proteins in primary GBM tissues. LRRC4 is negatively correlation with DEPTOR and LC3B expression. T tumour. c The quantitative analysis of LRRC4, DEPTOR and LC3B proteins expression in each primary GBM tissues (b). d The correlation analysis of LRRC4 and DEPTOR in Cohort 1 (Glioblastoma, TCGA, Cell 2013, left) and Cohort 2 (Glioblastoma Multiforme, TCGA, PanCancer Atlas, right) of GBM samples from TCGA database. e Statistical analysis of the expression of LRRC4 between recurrent and non-recurrent patients from the Oncomine Murat brain dataset. f Schematic diagram of the relationship among LRRC4, autophagy and TMZ chemosensitivity: when GBM cells without LRRC4 expression are attacked by TMZ treatment, DEPTOR directly binds and inhibits the phosphorylation of MTOR, thereby trigger protective autophagy to permit GBM cell survival. But, when GBM cells with LRRC4 expression are attacked by TMZ treatment, LRRC4 directly binds and promotes the degradation of DEPTOR. Degradation of DEPTOR leads to activation of MTOR, thereby inhibits protective autophagy, and finally induces apoptotic cell death.