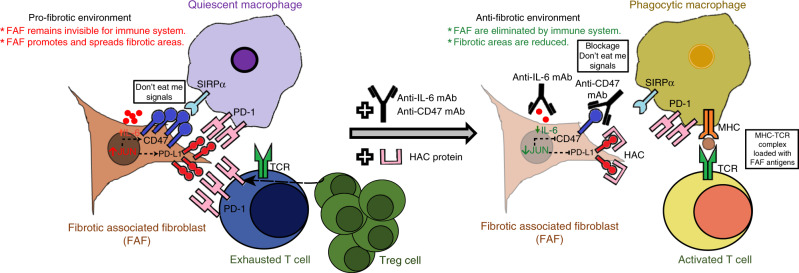
Fig. 7. Schematic diagram of the proposed mechanisms of fibrosis clearance.
Left: In fibrotic lung, we find persistent myofibroblast activation in fibrotic plaques and JUN upregulation. JUN expression in fibrosis-associated fibroblasts (FAFs) appears to directly control the promoters and enhancers of CD47 and CD274 (PD-L1). The direct consequence is increased expression of these immune-checkpoint proteins in fibroblasts and dormant macrophages which do not phagocytose, but continue to release chronic inflammatory cytokines. JUN also directly regulates IL-6 at the chromatin level. The increased expression and secretion of this potent cytokine leads to a suppressive adaptive immune response-chiefly T-cell exhaustion and upregulation of regulatory T cells. Right: Disrupting the suppression of the innate and adaptive immunity with CD47 and PD-L1 inhibitors as well as the proinflammatory IL-6 cytokine pathway stimulated phagocytic removal of pro-fibrotic fibroblasts and T-cell activation leading to clearance of the fibrosis in the lung.