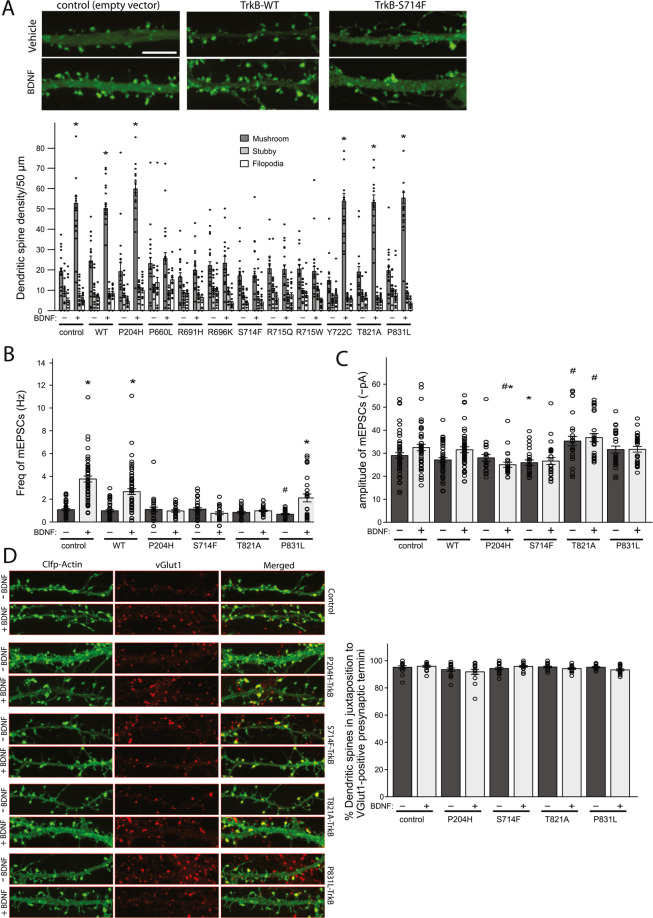
Figure 3.
Functional characterisation of TrkB mutants in neurons. (A). Primary dissociated hippocampal neurons were transfected with WT/mutant TrkB alongside Clover fluorescent protein (ClFP)-tagged actin and stimulated with either vehicle or recombinant BDNF. Dendritic spine density was assessed by confocal microscopy (upper panel: images from one mutant (S714F) shown. Scale bar: 10 μm); lower panel includes data from all mutants (number of spines per 50 μm of dendrite length; data point = one dendrite). *p < 0.01, student’s t-test, ± SEM. (B). Patch-clamp experiments were performed on rat hippocampal neurons transiently transfected with WT/mutant TrkB, before (−) and after (+) recombinant BDNF. Shown is the frequency of mEPSCs for all cells recorded. *indicates significant (p < 0.01) increase compared to unstimulated state; by one-way ANOVA-Tukey, F = 28.93. #indicates significant (p < 0.05) decrease compared to unstimulated control (baseline); by one-way ANOVA-Tukey, F = 15.4 ± SEM. (C). Shown is amplitude of mEPSCs for all cells recorded. *indicates significant (p < 0.05) reduction compared to BDNF-stimulated control; by one-way ANOVA-Tukey, F = 8.024. #indicates significant (p < 0.05) difference to unstimulated control; by one-way ANOVA-Tukey, F = 10.03. (D). Analysis of pre and post-synaptic correlation was done by transfection of ClFP-Actin (to highlight dendritic spines) and WT/mutant TrkB followed by immunostaining of presynaptic terminals with anti-vGlut1 before (−) and after (+) recombinant BDNF addition to DIV11. Representative images are shown in left panel and percentage of dendritic spines (stubby and mushroom) positive for vGlut1 positive presynaptic terminals is shown in right panel ± SEM.