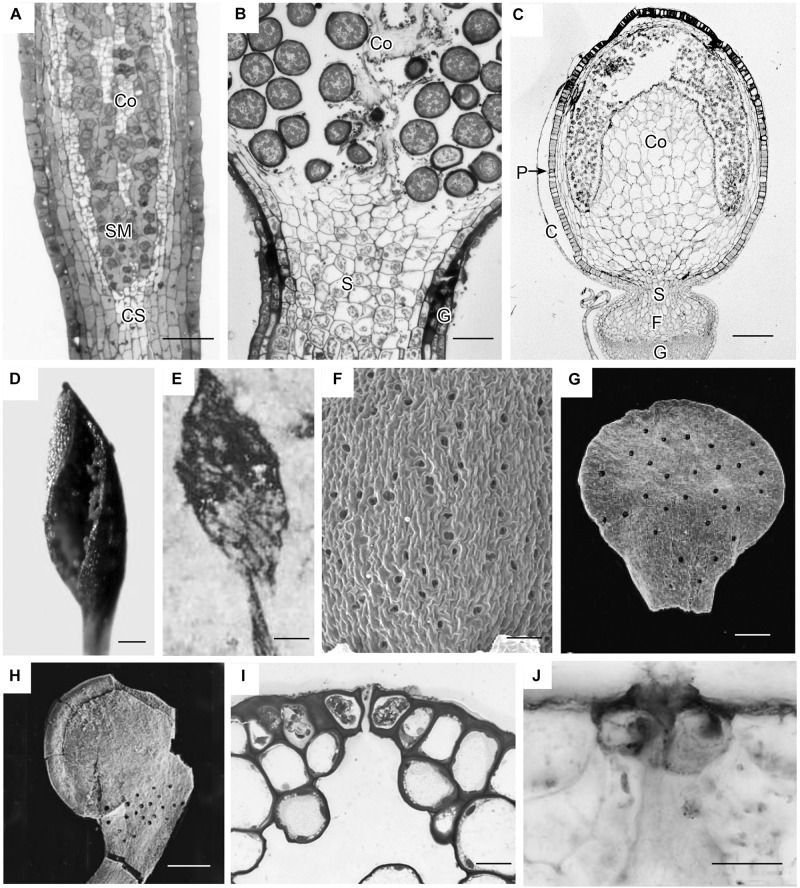
FIGURE 3.
Capsule anatomy, pseudostomata and stomata in extant members of early divergent moss lineages, and sporangia and stomata of the first fossil land plants. (A) Takakia ceratophylla. Light micrograph (LM) longitudinal section of solid cylindrical capsule with spore mother cells (SM), columella (Co) and conducting strand (CS) in seta. (B) Andreaea rothii. LM longitudinal section of solid capsule with spores, columella (Co) and short seta (S) surrounded by gametophyte (G) tissue of the pseudopodium. (C) Sphagnum tenellum. LM longitudinal section of solid capsule, covered by calyptra (C), with pseudostomata (P) in the epidermis, massive columella (Co) covered by the spore sac, and highly reduced seta (S) embedded by foot (F) into gametophyte (G) pseudopodium. (D) Takakia ceratophylla capsule with single spiraled suture and spores. (E) Tortilicaulis transwalliensis capsule from the Silurian resembles Takakia in (D). (F) Sphagnum tenellum SEM showing scattered pseudostomata on dried capsule. (G) Early Devonian bivalved sporangium with scattered stomata (spots). (H) Early Devonian sporangium with band of stomata (spots) at base. (I) Oedipodium LM cross section of neck with guard cells with ledges over substomatal cavity. (J) Aglaophyton major from Rhynie Chert. Cross section of mature axis with stoma showing guard cells with ledges over substomatal cavity. Fossil images reproduced with permission from Journal of Experimental Botany (Edwards et al., 1998) and Paleontology (Edwards, 1979). Bars: (A,E,H) = 100 μm; (B,G,J) = 50 μm; (C,F) = 500 μm; (D)= 200 μm, (I) = 20 μm.