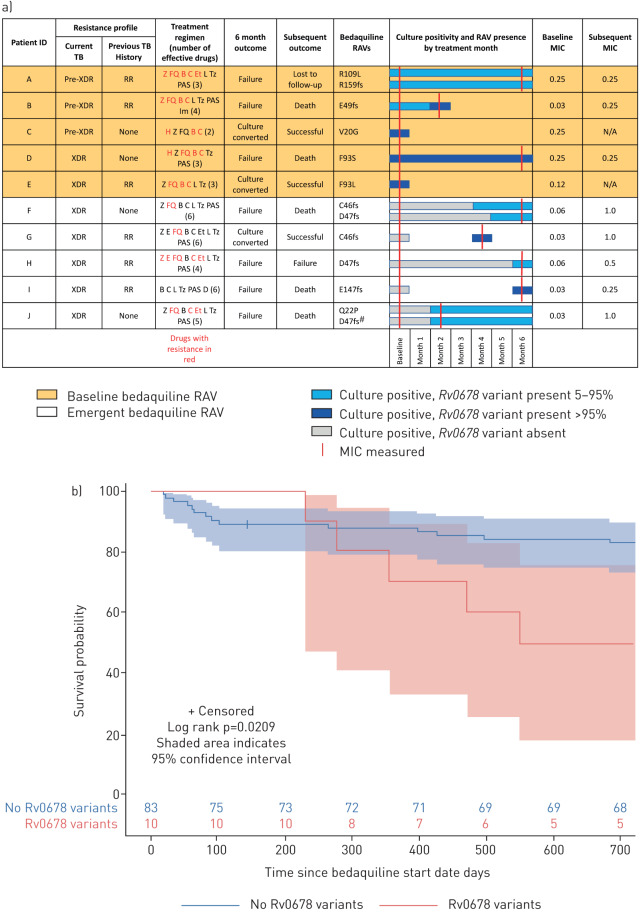
FIGURE 1.
a) Patients with Rv0678 mutations in positive tuberculosis (TB) sputum cultures. Resistance profiles are for the current and most recent previous TB episodes. Drugs used in treatment regimen are indicated, with those ineffective due to resistance coloured red. H: isoniazid; Z: pyrazinamide; E: ethambutol; FQ: fluoroquinolones; B: bedaquiline; C: clofazimine; Et: ethionamide; L: linezolid; T: terizidone; PAS: p-aminosalicylic acid; D: delamanid; Im: imipenem; RAV: resistance-associated variant; XDR: extensively drug resistant; RR: rifampicin resistant. Patient A was phenotypically ethionamide resistant in the absence of ethionamide resistance-associated variants. Rv0678 variants are categorised as baseline (orange background) or emergent (white background). Amino acid changes at variant sites are specified (fs, frameshift mutation). Bars indicate culture-positive samples without variants (grey), heterozygous variants (light blue) and fixed variants (dark blue). Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) are shown at baseline and at subsequent time-point if performed (red lines). #: in patient J, six further low-frequency Rv0678 variants appeared at 6 months (A57E, R72 T, D88fs, D88A, G121R, L122P). b) Kaplan–Meier curve for survival probability following initiation of bedaquiline therapy with censoring for loss to follow-up. Shaded area indicates 95% confidence interval.