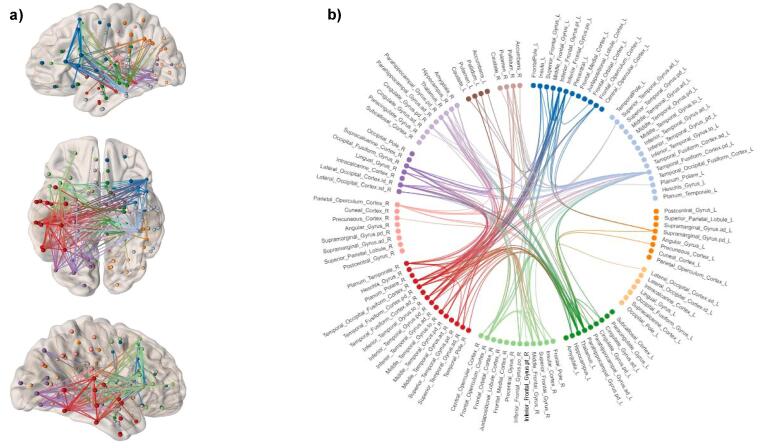
Fig. 4.
Non-parametric network based statistics (NBS) analysis results showing a graph sub-component comprising 153 edges (p < 0.01) where the ADD group demonstrated significantly less connectivity compared to the CON group during the gain > neutral anticipation contrast of the MID task. Graph sub-components were identified among all node pairwise connections with a t-statistic threshold of t > 3.1, corrected for multiple comparisons, while controlling for study site using permutation (5000) analyses. Reductions in connectivity in the ADD group are represented by a) brain connectivity maps and b) a circular connectogram. Brain regions are grouped on the connectogram circumference according to lobes and centres in the left and right hemispheres (left frontal [dark blue]; left temporal [light blue]; left parietal [dark orange], left occipital [light orange]); left limbic [dark green]; right frontal [light green]; right temporal [dark red]; right parietal [pink]; right occipital [dark purple]; right limbic [light purple]; left striatal [dark brown] and right striatal [light brown]. Brain connectivity maps and the circular connectogram were generated using NeuroMArVL (http://immersive.erc.monash.edu.au/neuromarvl). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)