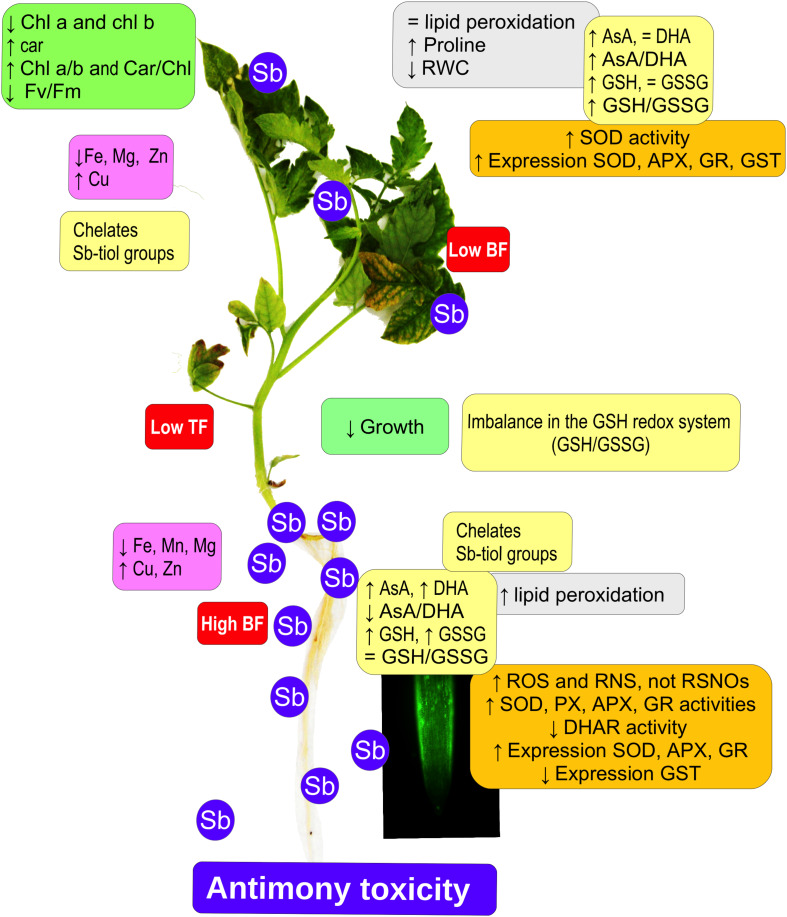
FIGURE 7.
Model showing the effect of antimony toxicity on tomato roots and leaves. There is reduced growth of roots and stems, and chlorosis and necrosis in the leaves. Chlorophyll levels decline but carotenes increase, with a decrease in photosynthetic efficiency. The accumulation of Sb occurs mainly in the roots, and the absorption and accumulation of other metallic elements is altered. Gene expression and antioxidant enzyme activities both increase. There are increases in ROS and RNS, except for nitrosothiols. The AsA/GSH cycle is disrupted, affecting redox homeostasis.