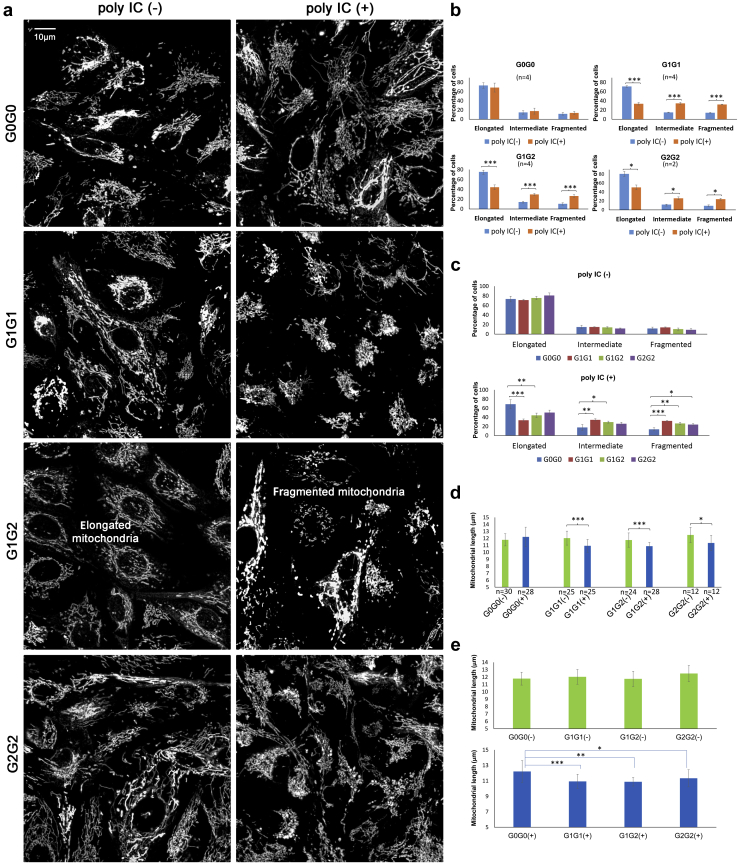
Figure 4.
Mitochondrial morphology in live primary proximal tubule cell lines (PTCs) from African American individuals with different APOL1 genotypes cultured in growth media without (−) and with (+) polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid (poly IC). Primary PTC lines were from 7 African American individuals (2 homozygous for APOL1 G0, 2 homozygous for G1, 2 for compound G1/G2), and 1 homozygous for G2. Cells were grown without (−) or with (+) 2.5 μg/ml poly IC for 16 hours in full Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium. Cells were subsequently incubated for 30 minutes with a final concentration of 50 nM MitoTracker Red (Invitrogen). (a) Representative images reveal that renal PTCs from the G0 homozygotes had similar mitochondrial morphology when incubated with (+) or without (−) poly IC. However, primary PTCs from G1 and G2 homozygotes and G1/G2 compound heterozygotes displayed more fragmented mitochondria when incubated with (+) poly IC than those without (−) poly IC. Each representative image was a compression of a series of z-stack scans, clearly capturing mitochondrial morphology. Binary images displayed with enhanced local contrast (CLAHE) via Fiji scoring by Mitochondrial Network Analysis. (b) Paired comparisons showing that the percentage of cells with mitochondrial elongation significantly decreased and the percentage of cells with mitochondrial fragmentation significantly increased in primary renal PTCs with (+) poly IC than without (−) poly IC in subjects homozygous for G1, homozygous for G2, and compound G1/G2 heterozygotes. The percentage of cells with mitochondrial elongation and fragmentation did not differ in primary PTCs homozygous for G0. For each primary PTC line, 2 independent experiments were performed to image mitochondrial networks with or without poly IC. Primary PTCs from 2 African American individuals (1 woman and 1 man of comparable age) were selected for homozygous G0, homozygous G1, and compound G1/G2 genotypes. Only 1 homozygous G2 (female) had available primary PTCs. (Note: n refers to number of independent cell culture experiments; ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗ P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 throughout Figure 4; no statistical significance was found in any other paired comparison.) (c) Paired comparisons showing that the percentage of cells with mitochondrial elongation was significantly lower, and the percentage of cells with mitochondrial fragmentation significantly higher, in primary renal PTCs from G1 homozygotes and G1/G2 compound heterozygotes versus G0 homozygotes with poly IC in growth media. The effect in G2 homozygotes may have been limited by statistical power (1 individual, 2 independent experiments). The percentage of cells with mitochondrial elongation and fragmentation did not differ in primary PTCs of different APOL1 genotypes without poly IC. (d) Paired comparisons showing that mitochondrial length significantly decreased in primary renal PTCs with (+) poly IC versus without (−) poly IC in primary PTCs homozygous for G1, homozygous for G2 and compound G1/G2 heterozygotes; however, mitochondrial length did not differ in homozygous G0 primary PTCs with (+) or without (−) poly IC. n refers to the total number of images captured for Mitochondrial Network Analysis. At least 6 z-stack images were taken for each independent cell culture experiment. For cells of each PTC line, 2 independent experiments were performed for imaging mitochondrial networks with or without poly IC. Primary PTCs from 2 different African American individuals were selected for G0 homozygotes, G1 homozygotes, and compound G1/G2 heterozygotes; no significant difference in mitochondrial morphology (mitochondrial length defined as rods/network branches in μm) was observed between the 2 individuals of the same APOL1 genotype with or without poly IC. Only 1 G2 homozygote had available primary PTCs. (e) Mitochondrial length was comparable across primary PTCs with different APOL1 genotypes without poly IC. However, when cells were incubated with low-dose poly IC (2.5 μg/ml) for 16 hours, those possessing 2 APOL1 KRVs (homozygous G1, homozygous G2, and G1/G2 compound heterozygotes) appeared to have decreased mitochondrial length (more fragmented mitochondria were present).